产品号 #100-0711_C
人NK细胞培养扩增试剂盒
在无血清条件下持续扩增自然杀伤(NK)细胞,不使用可能带来后续问题的饲养层细胞。
使用ImmunoCult™NK细胞扩增试剂盒,为高倍数扩增NK细胞提供优化的培养条件。该试剂盒包括ImmunoCult™NK细胞基础培养基,ImmunoCult™NK细胞扩增补充剂,和ImmunoCult™NK细胞扩增包被材料,为您提供完整且方便操作的培养体系。仅培养14天后,细胞就可以直接用于下游应用。
该试剂盒与我们的许多其他上下游产品兼容。例如,您可以使用EasySep™细胞分选试剂盒分选NK细胞,之后立即使用ImmunoCult™NK细胞扩增试剂盒扩增。
亚型
专用培养基
细胞类型
NK 细胞
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,扩增
品牌
ImmunoCult
研究领域
癌症,免疫,细胞治疗开发
制剂类别
Animal Component-Free,无血清,Xeno-Free
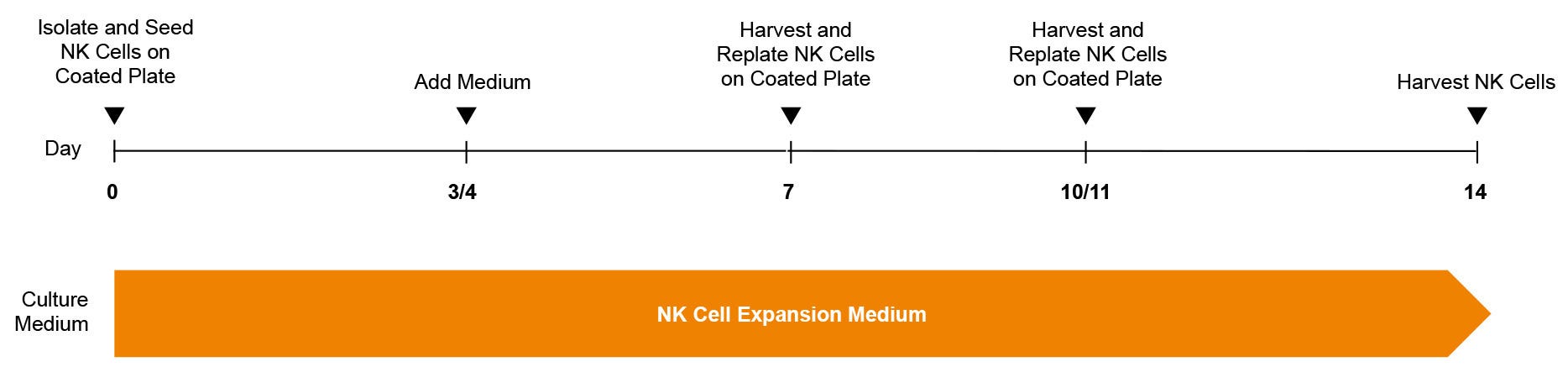
Figure 1. ImmunoCult™ NK Cell Expansion Protocol
Human natural killer (NK) cells are isolated from blood or leukapheresis using EasySep™ selection. The NK cells are cultured in ImmunoCult™ NK Cell Expansion Medium, on plates coated with ImmunoCult™ NK Cell Expansion Coating Material. After 3 days, fresh medium is added to the culture. On day 7, and again on day 10 or 11, expanding NK cells are harvested and replated on freshly coated plates. Expanded NK cells were harvested on day 14 for use in downstream assays.
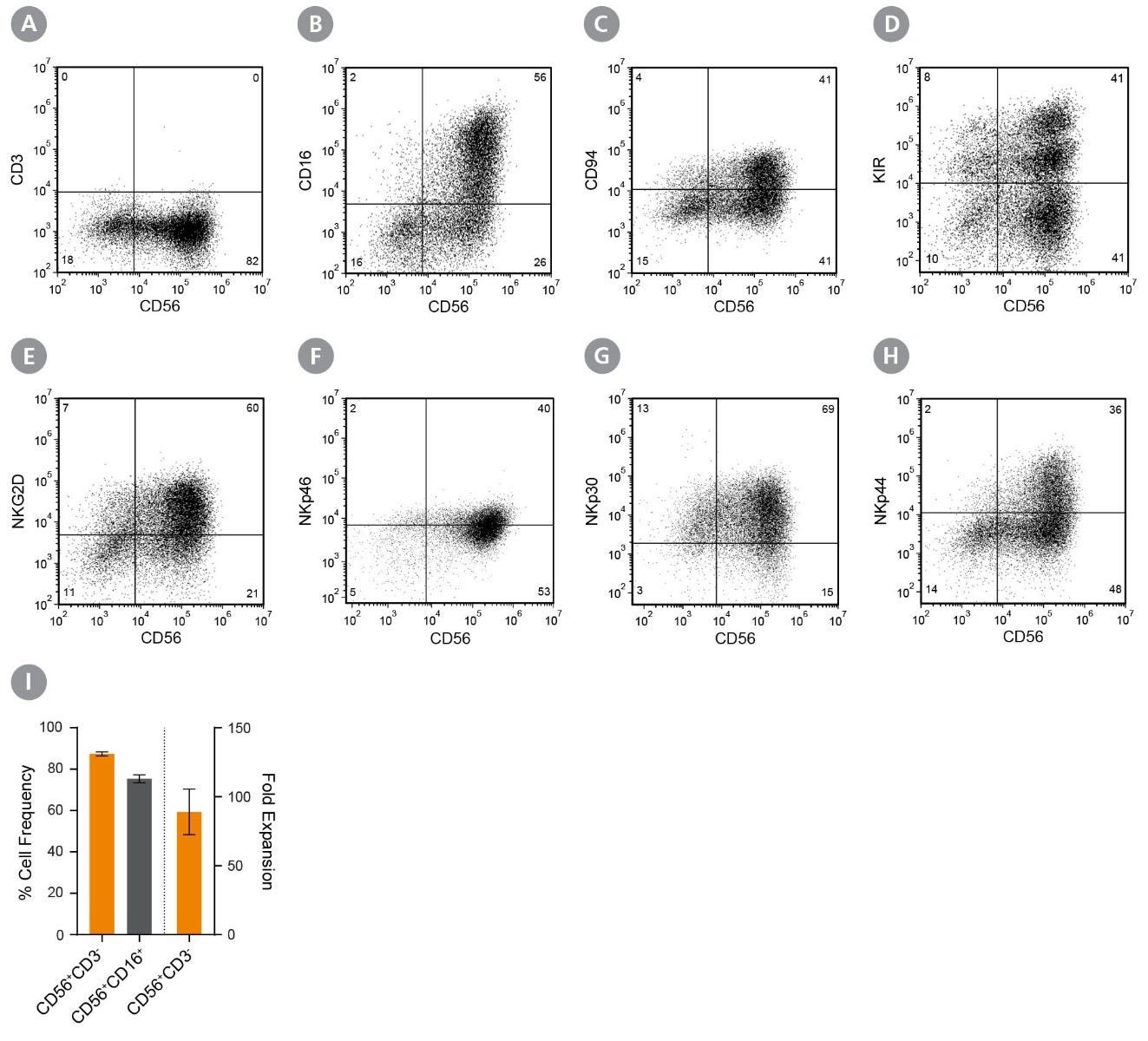
Figure 2. CD56+CD3− NK Cells Expand Over 14 Days in Feeder- and Serum-Free Culture Conditions
Isolated human CD56+CD3− NK cells were cultured using ImmunoCult™ NK Cell Expansion Kit for 14 days (Figure 1). Cells were harvested and analyzed for expression of characteristic NK cells markers, including CD56, CD3, CD16, CD94, KIR, NKG2D, NKp46, NKp30, and NKp44 by flow cytometry. Staining for killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) molecules was performed using two different antibody clones, HP-MA4 and 180704, which recognize distinct KIR molecules. Dead cells were excluded by light-scatter profile and DRAQ7™ staining. (A - H) Representative flow cytometry plots. (I) The average frequencies of viable CD56+CD3− and CD56+CD16+ NK cells on day 14 were 87 ± 1% and 75 ± 2%, respectively. The average fold expansion of CD56+CD3− cells was 89 ± 17. Results shown represent mean ± SEM (n = 34).
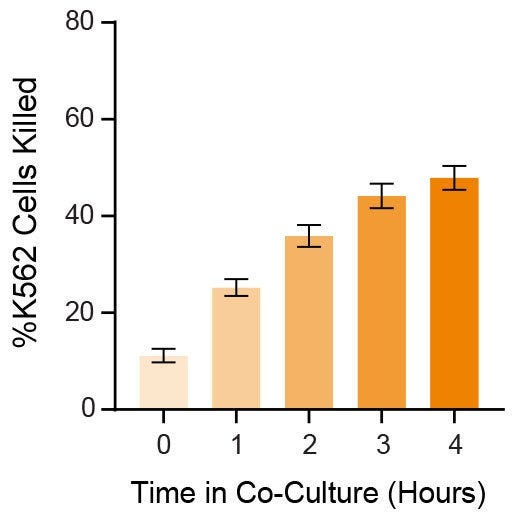
Figure 3. Expanded NK Cells Are Functional, Killing K562 Cells in Co-Culture
Isolated CD56+CD3− NK cells were expanded as described in Figure 1. Expanded NK cells were co-cultured with Incucyte® Cytolight Rapid Dye-labeled K562 cells at 1:1 ratio of NK:K562 cells at 37°C for 4 hours. Incucyte® Caspase-3/7 Dye, a caspase-inducible dye, was added to the co-culture to detect caspase-induced apoptosis of the K562 cells. Images were obtained every hour using the Incucyte® imaging system and then analyzed to determine % killing (# apoptotic K562 cells ÷ # total labeled K562 cells). After 4 hours, an average of 48 ± 2.4% K562 cells were killed (n = 9). Data represent mean ± SEM.
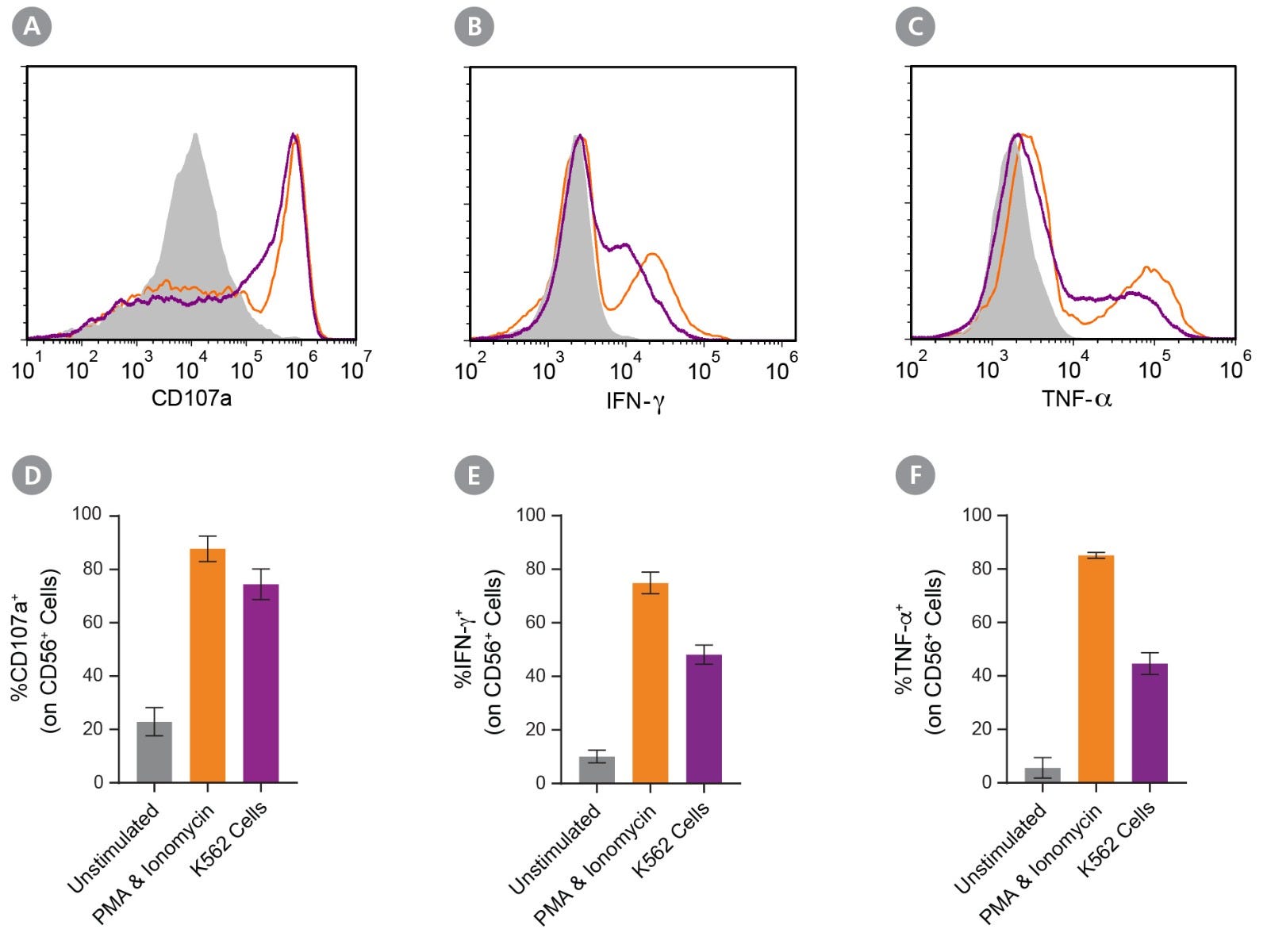
Figure 4. Expanded NK Cells Degranulate and Produce Cytokines After Stimulation
Isolated CD56+CD3− NK cells were expanded for 14 days (Figure 1). Expanded NK cells were left unstimulated (control) or were stimulated with either phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin or K562 cells at a ratio of 1:1 effector:target cells. CD107a antibody was added, and cultures were incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. After the first hour, Monensin and Brefeldin A were added. Cells were assessed for surface CD56, CD107a, and intracellular IFN-γ and TNF-α expression by flow cytometry. (A-C) Representative histograms of CD107a, IFN-γ, and TNF-α expression of unstimulated (grey filled), PMA and ionomycin-stimulated (orange), and K562-stimulated (purple) NK cell samples. (D) The average frequency of NK cells expressing surface CD107a, a marker of degranulation, was 23 ± 5% for the unstimulated control, 88 ± 5% after stimulation with PMA and ionomycin, and 74 ± 6% after stimulation with K562 cells. (E) The average frequency of NK cells expressing intracellular IFN-γ was 10 ± 2% for the unstimulated control, 75 ± 4% for cells stimulated with PMA and ionomycin, and 48 ± 4% for cells co-cultured with K562 cells. (F) The average frequency of NK cells expressing intracellular TNF-α was 6 ± 4% for the unstimulated control, 85 ± 1% cells stimulated with PMA and ionomycin, and 45 ± 4% for cells co-cultured with K562 cells. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 6 - 13).
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Species | Human |
|---|---|
| Formulation Category | Animal Component-Free, Serum-Free, Xeno-Free |

人CD56+细胞的免疫磁珠正选
免疫磁珠负选不带标记的人NK细胞

用于体外诊断(IVD)应用的密度梯度离心管
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。