产品号 #09950_C
用于淋系祖细胞向NK细胞分化的添加物
Serum-free medium for culture and expansion of hematopoietic cells
Pyrimido-indole derivative that enhances HSC self-renewal in vitro
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
StemSpan™ NK细胞分化添加物(100X)能支持淋系祖细胞向自然杀伤(NK)细胞分化。
该添加物是StemSpan™ NK细胞生成试剂盒或STEMdiff™ NK细胞分化试剂盒的组分之一,也可单独购买以方便您的使用。可使用该添加物将CD34+细胞在含StemSpan™淋系祖细胞扩增添加物(10X)的StemSpan™ SFEM II培养基中、在StemSpan™淋系分化包板材料(100X)包被的培养板上分化产生的淋系祖细胞进一步分化为NK细胞。
StemSpan™NK细胞分化添加物(100X)需与StemSpan™ SFEM II和UM729搭配使用以促进向CD56+ NK细胞的分化。
关于NK细胞生成方法的详细信息,请参阅技术手册。
Subtype
Supplements
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells, NK Cells
Species
Human
Application
Differentiation
Brand
StemSpan
Area of Interest
Cancer, Immunology, Stem Cell Biology
Formulation Category
Serum-Free
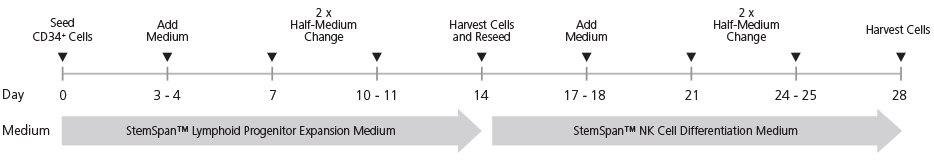
Figure 1. StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Protocol
CB-derived CD34+ cells are seeded on day 0. Medium should be topped up after 3 - 4 days of culture followed by two half-medium changes every 3 - 4 days. On day 14, cells at the lymphoid progenitor stage are harvested and reseeded for further differentiation into NK cells. Top-up and half-medium changes should be performed every 3 - 4 days after harvest and reseed, as indicated in the figure. Note: UM729 should only be added to the NK Cell Differentiation Medium, but not the Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium.
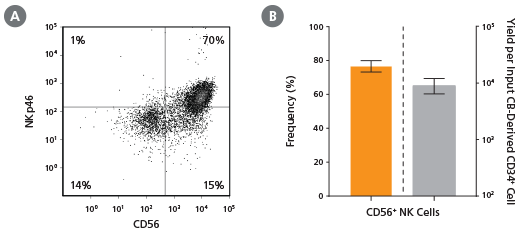
Figure 2. Frequency and Yield of CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
CB-derived CD34+ cells (freshly isolated or frozen) were cultured with the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit for 28 days as described. Cells were harvested and analyzed for (A,B) CD56 and (A) NKp46 expression by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and viability staining. (B) The average frequency of viable CD56+ NK cells on day 28 was 77%, with ~9,000 CD56+ cells produced per input CB-derived CD34+ cell. Shown are means with 95% confidence intervals (n = 45: 23 freshly isolated and 22 frozen CD34+ cell samples). BM-derived CD34+ cells were also differentiated into NK cells using the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit. The yield of NK cells from BM HSPCs is typically lower than with CB, averaging ~75 per input CD34+ cell (n = 3, data not shown).
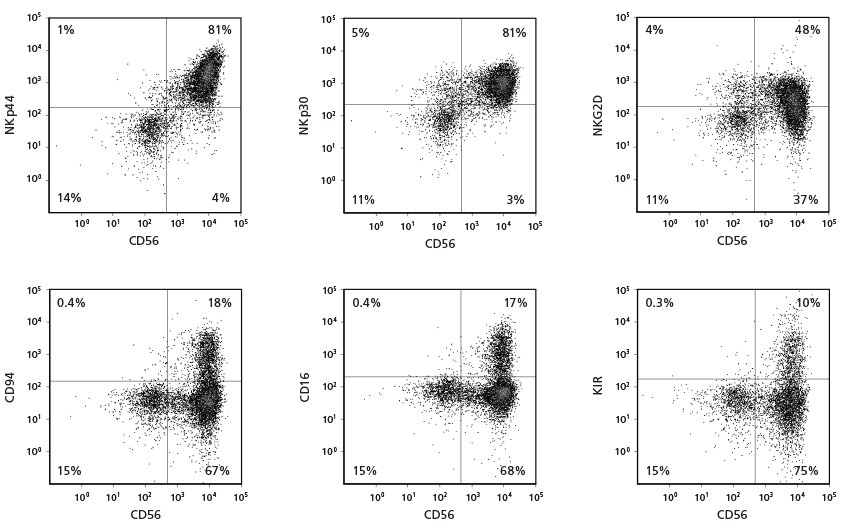
Figure 3. Cell Surface Marker Expression on CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
CB-derived CD34+ cells were cultured with the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit for 28 days. The differentiated cells were harvested and analysed by flow cytometry for the expression of CD56, NKp44, NKp30, NKG2D, CD94, CD16, and KIR. Staining for KIR molecules was performed using a combination of two clones for the antibody, 180704 and HP-MA4, as each recognizes a distinct subset of KIR molecules.
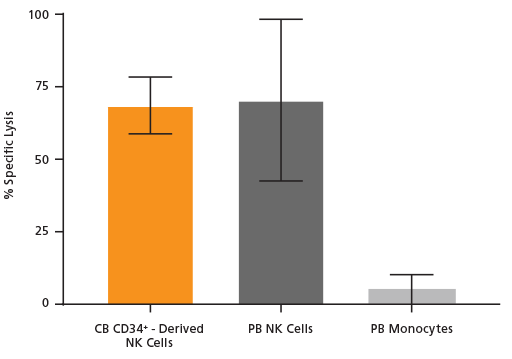
Figure 4. Cultured NK Cells Exhibit Cytotoxicity Toward K562 Cell Line
NK cells were generated from CB-derived CD34+ cells over 28 days using the protocol in Figure 1. On day 28, cells were harvested, stained for CD56, and viable CD56+ cells were counted. K562 cells were incubated with 8 μM calcein AM at 37°C for 1 hour and then washed twice. CD56+ NK cells were then combined with 10,000 of these calcein AM-labeled K562 target cells at an Effector:Target ratio of 5:1 in U-bottom 96-well plates and co-cultured at 37°C for 4 hours. Adult peripheral blood (PB) NK cells and monocytes isolated using EasySep™ were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. PB NK cells were cultured overnight with the NK Cell Differentiation Supplement and SFEM II, while PB monocytes were cultured overnight in SFEM II only. To detect spontaneous release, control wells containing only calcein AM-labeled K562 target cells were set up. The labeled K562 cells were treated with 1% Triton™ X-100 to measure maximum release. After incubation, plates were centrifuged at 500 x g for 5 minutes and 100 μL of supernatant was transferred to black plates and analyzed using a SpectraMax® microplate reader (excitation 485 nm/emission 530 nm). Results are expressed as % specific lysis: [(test release - spontaneous release) x 100] / (maximum release - spontaneous release). CB CD34+-derived NK cells show similar killing activity toward K562 target cells compared to PB NK cells. Shown are means ± SD (CB CD34+-derived NK cells: n = 18, PB NK cells and monocytes: n = 7).
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Species | Human |
|---|---|
| Formulation Category | Serum-Free |
用于人CD34+细胞扩增及分化为淋系祖细胞的添加物

用于淋系祖细胞扩增与分化的包板材料

小鼠抗人CD56 (NCAM)单克隆IgG1抗体

冻存的人原代细胞
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。

