产品号 #05220_C
Defined, xeno-free induction medium for early mesodermal differentiation
Defined, xeno-free induction medium for early mesodermal differentiation

Feeder-free, animal component-free culture medium for maintenance of human ES and iPS cells
cGMP, enzyme-free cell dissociation reagent
RHO/ROCK pathway inhibitor; Inhibits ROCK1 and ROCK2

cGMP, feeder-free maintenance medium for human ES and iPS cells
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium (MIM) is a defined, xeno-free medium for generation of early mesoderm cells from human embryonic stem (ES) and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. Protocols for mesodermal differentiation can be difficult and inconsistent, therefore, use the short and simple STEMdiff™ MIM monolayer protocol to differentiate your human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs).
STEMdiff™ MIM is a complete medium that produces a cell population enriched for early mesoderm, as indicated by positive expression of Brachyury (T) and NCAM markers. As part of the hPSC workflow, STEMdiff™ MIM efficiently differentiates hPSCs cultured in TeSR™ media. When directed, early mesoderm cells produced using STEMdiff™ MIM can be further differentiated to specialized cell types, such as osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes or endothelial cells. For more information, see the data below.
Subtype
Specialized Media
Cell Type
Mesoderm, PSC-Derived, Pluripotent Stem Cells
Species
Human
Application
Cell Culture, Differentiation
Brand
STEMdiff
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
Formulation Category
Serum-Free, Xeno-Free
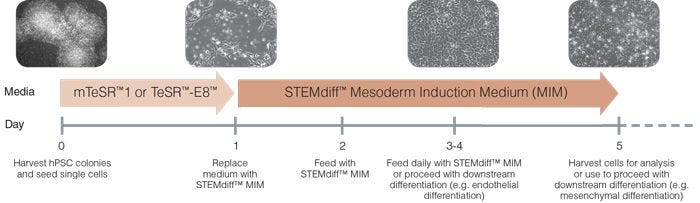
Figure 1. Schematic of Mesoderm Induction Medium Differentiation Timeline
On day 0, hPSC colonies are harvested and seeded as single cells at 5 x 10 4 /cm 2 in mTeSR™1 or TeSR™-E8™ and supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632. TeSR™ medium is replaced on day 1 with STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium when cells are at approximately 20 - 50% confluency. Cells are then fed daily and cultured in STEMdiff™ MIM (days 2-4). Cells can be transferred to downstream differentiation conditions between days 3 - 5 or collected on day 5 for analysis.
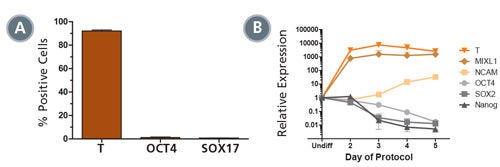
Figure 2. STEMdiff™ MIM Generates a Homogenous Population of T + OCT4 - Early Mesoderm
(A) Data showing marker expression characteristic of the early mesoderm (positive Brachyury (T) expression and negative OCT4 and SOX 17 expression) on day 5 of the protocol. Data is expressed as a mean percentage of cells expressing each marker ± SD, n = 33 (T, OCT4), n = 5 (SOX17). (B) Expression of undifferentiated cell markers (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG) and early mesoderm markers (T, MIXL1, NCAM), measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and normalized to levels in undifferentiated cells, n = 2.
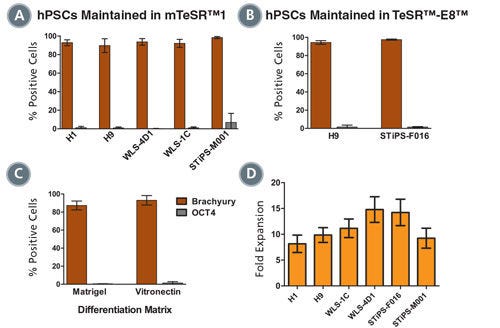
Figure 3. Mesoderm Differentiation and Cell Expansion are Efficient and Comparable Across Multiple hPSC Cell Lines
Graphs show mesoderm formation in multiple human ES (H1 and H9) and iPS (WLS-4D1, WLS-1C, STiPS-M001 and STiPS-F016) cell lines as measured by expression of Brachyury (T) and absence of OCT4. Cells maintained in (A) mTeSR™1 or (B) TeSR™-E8™ medium were differentiated using STEMdiff™MIM. (A, n = 2 - 10 per cell line, B, n = 3, data are expressed as a mean percentage ± SD) (C) Mesoderm differentiation on Corning® Matrigel® or Vitronectin XF™ is comparable. (n = 5, data are the mean percentage ± SD) (D) Average fold expansion of cells cultured in STEMdiff™MIM, as determined by cell yield / cells seeded. (n = 3 - 13. Error bars indicate SEM)
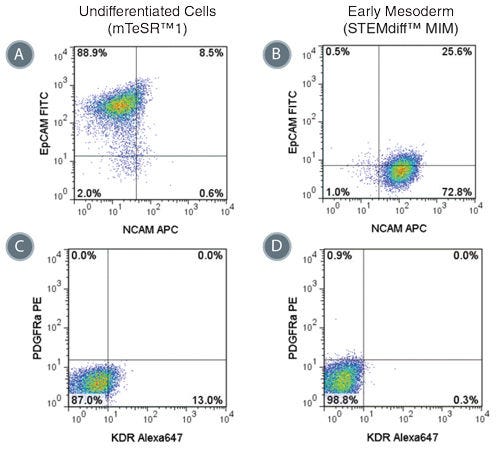
Figure 4. Phenotype of Cells Treated with STEMdiff™ MIM is Consistent with Early Mesoderm
Representative flow cytometry plots showing the switch from (A) EpCAM + NCAM -/low in hPSCs cultured in mTeSR™1 to (B) EpCAM -/low NCAM + expression in STEMdiff™ MIM-treated cells (day 5). EpCAM -/low NCAM + expression is characteristic of the early mesoderm. Expression of PDGFRα and KDR are low in both (C) hPSCs cultured in mTeSR™1 and (D) early mesoderm cells derived with STEMdiff™ MIM.
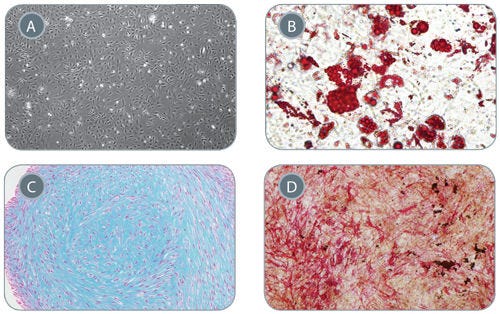
Figure 5. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Early Mesoderm Cells Can Be Further Differentiated in In Vitro Assays
(A) Early mesoderm cells generated with the 5-day STEMdiff™ MIM protocol and subsequently cultured with MesenCult™-ACF develop mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like morphology, 40X magnifi cation. MSC-like cells can subsequently differentiate into (B) adipocytes (Oil Red O staining), 200x magnification, (C) chondrocytes (Alcian Blue staining), 100X magnification, and (D) osteogenic cells (Fast Red and Silver Nitrate staining), 40X magnification.
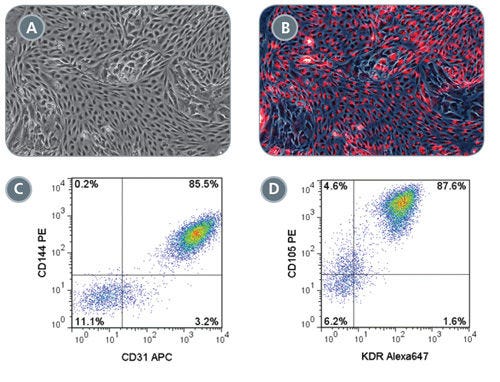
Figure 6. Robust Endothelial Differentiation of STEMdiff™ MIM-Generated Early Mesoderm Cells
On day 3 of the STEMdiff™ MIM protocol, early mesoderm cells were switched to a downstream endothelial differentiation protocol based on Tan et al. (A) Differentiated cells display characteristic endothelial cell morphology and (B) are able to uptake Dil-Ac-LDL (red). Representative flow cytometry plots showing (C) 85.5% CD144 + CD31 + and (D) 87.6% CD105 + KDR + expression in differentiated endothelial cells.
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。

