产品号 #08620_C
用于从人多能干细胞高效生成背侧前脑神经类器官的细胞培养基试剂盒
用于从人多能干细胞高效生成背侧前脑神经类器官的细胞培养基试剂盒
利用人类多能干细胞,无需基质嵌入,即可稳定地生成三维、具有区域模式的脑类器官培养物。STEMdiff™ 背侧和腹侧前脑类器官分化试剂盒采用无血清细胞培养基,可与 AggreWell™ 生成的拟胚体配合使用,防止类器官融合,并实现每套试剂盒生成超过 500 个以上高重复性的类器官。该试剂盒基于 Sergiu Paşca 团队的方法开发(参考文献:F. Birey 等,Nature,2017),可生成具有代表性人类前脑发育特征的三维体外模型,具有相应的细胞组成与结构组织。STEMdiff™ 背侧前脑类器官分化试剂盒(货号 #08620)可生成早期发育的背侧大脑皮层组织,而 STEMdiff™ 腹侧前脑类器官分化试剂盒(货号 #08630)可生成早期发育的腹侧大脑皮层下组织。利用这些试剂盒生成的类器官还可通过共培养形成 assembloids(组合类器官),用于研究不同脑区之间的相互作用(参考文献:F. Birey 等,Nature,2017)。若需进行超过 50 天的长期类器官培养,推荐使用 STEMdiff™ 神经类器官维持试剂盒(目录号 #100-0120)中的相关培养成分。
亚型
专用培养基
细胞类型
神经细胞,PSC衍生,神经干/祖细胞,多能干细胞
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,鉴定,分化,功能学筛选,免疫荧光,类器官培养,表型鉴定,球状体培养
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,神经科学,类器官
制剂类别
无血清
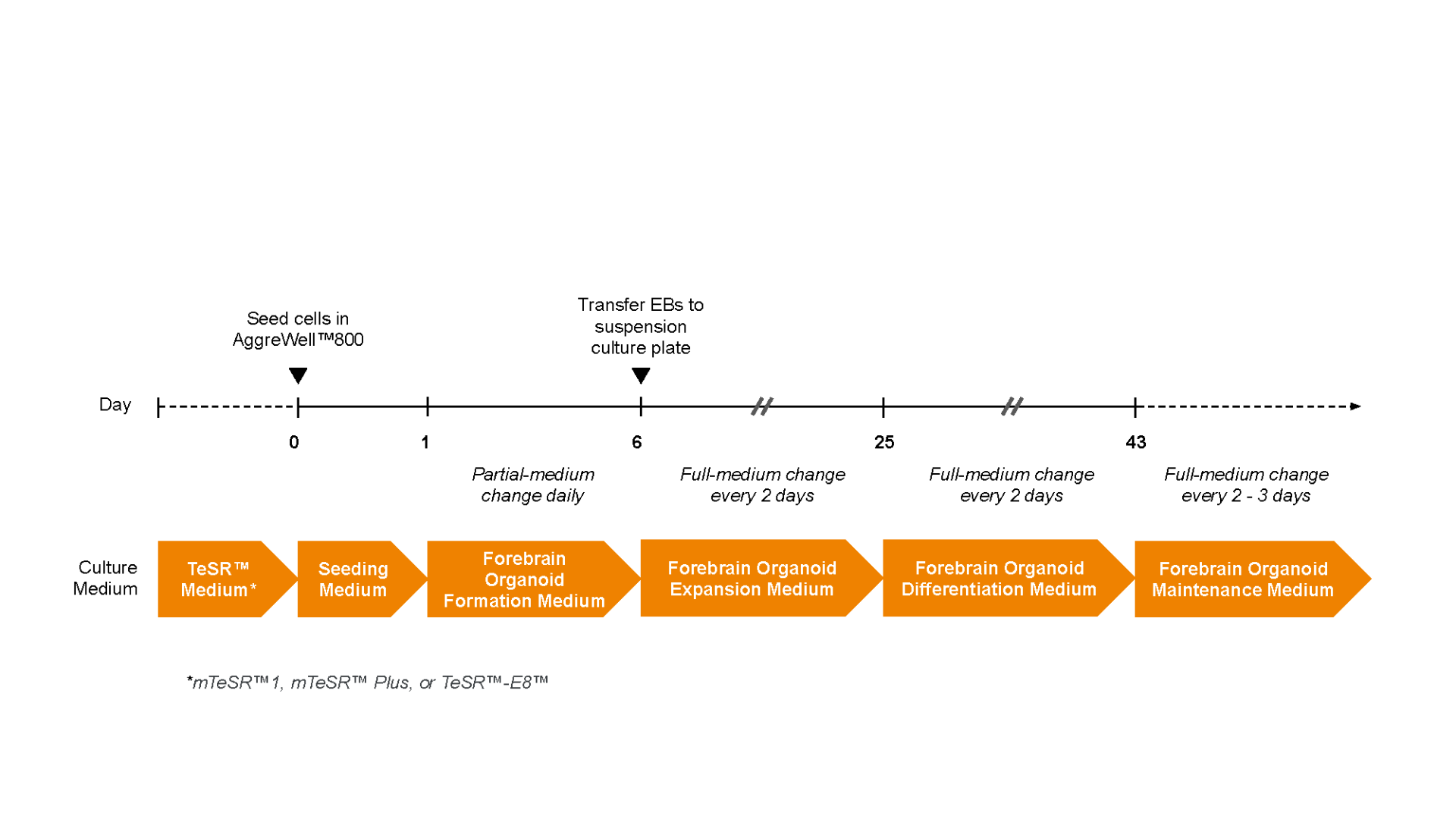
Figure 1. Schematic for the STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit
Human ES or iPS cell-derived dorsal forebrain organoids can be generated in 43 days. Embryoid bodies can be created in 6 days with AggreWell™800 plates. The EBs are then cultured in suspension, allowing growth and subsequent patterning to the dorsal forebrain. For the long-term maintenance and further maturation of dorsal forebrain organoids, see the PIS.
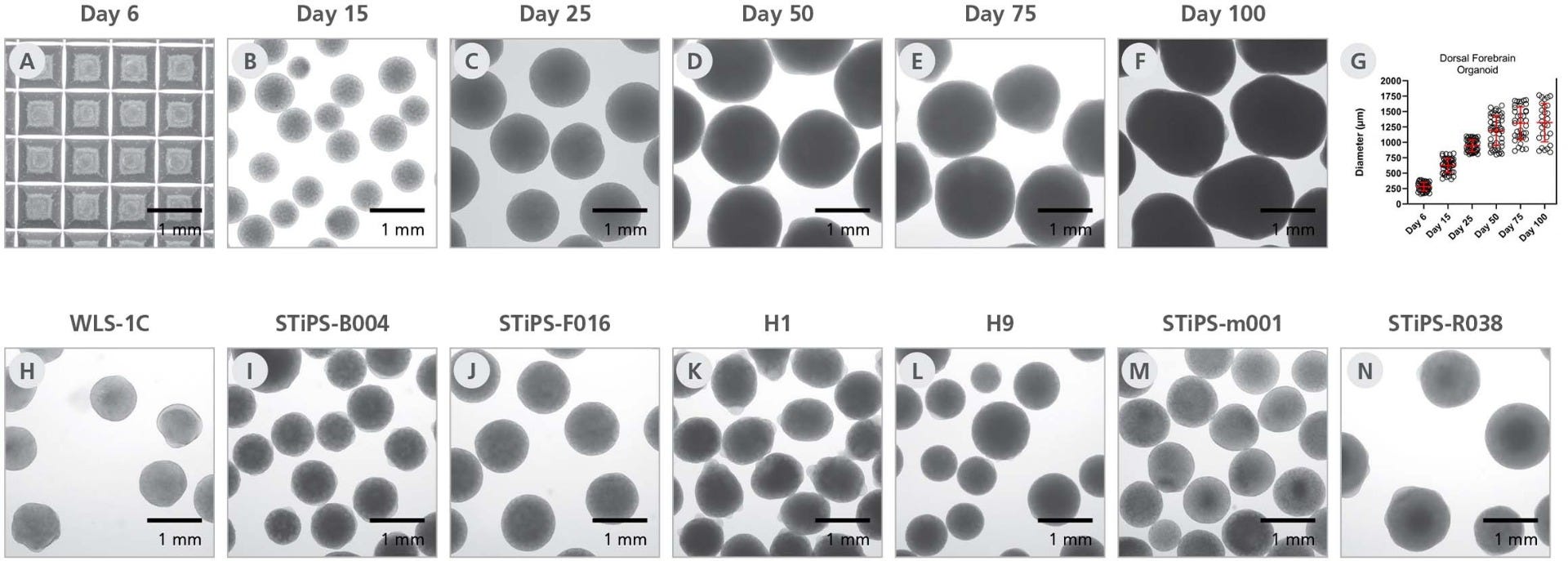
Figure 2. STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit Supports the Generation of Homogeneous, Reproducible Neural Organoids
(A) Neural aggregates formed in AggreWell™800 microwell plates exhibit uniform size and shape at day 6. H9-derived dorsal forebrain organoids from a single batch have spherical morphology at days (B) 15 (C) 25 (D) 50 (E) 75 and (F) 100. Scale bar = 1 mm. (G) Dorsal forebrain organoids exhibit homogeneous size over multiple cell lines (average ± SD, using 11 cell lines with 3 - 5 organoids counted per cell line and time point). (H-N) Day 25 organoids generated by a novice user with STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit show reproducibility across different cell lines.
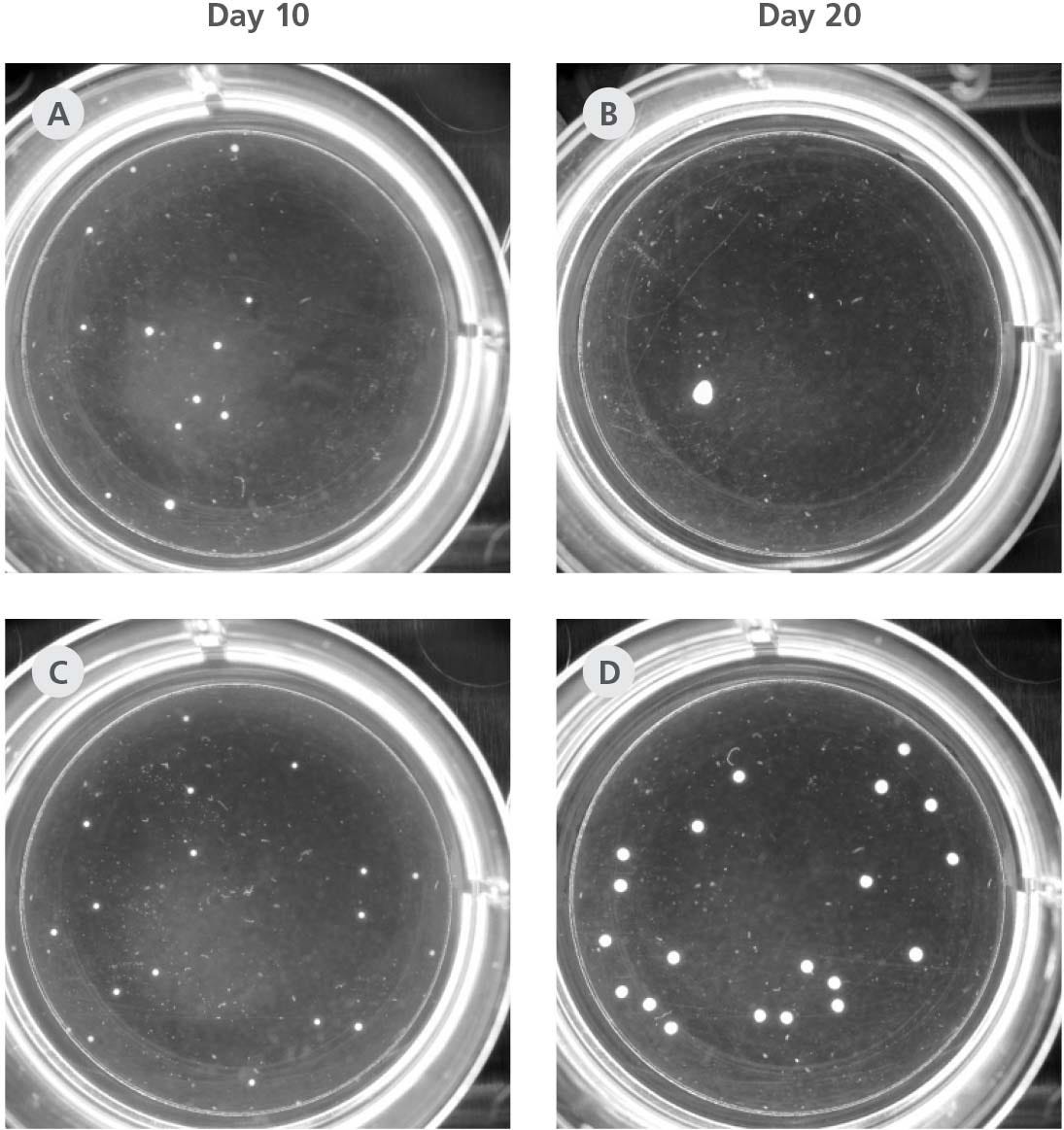
Figure 3. STEMdiff™ Dorsal and Ventral Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kits Reduce Unwanted Organoid Fusion
Whole-well images of dorsal forebrain organoid cultures derived from the H9 cell line in STEMdiff™ Forebrain Organoid Expansion Medium (bottom row) vs. the control published formulation (top row) show the extent of fusion typical in control media without orbital shaking. At Day 10 post-seeding in the control formulation, 12/12 organoids that were seeded are developing, but by Day 20 a single, larger organoid can be seen in the well. In STEMdiff™ Forebrain Organoid Expansion Medium, 20/20 seeded organoids are developing and 20/20 are still developing at Day 20 without shaking. While organoids in both culture conditions grow larger between 10 and 20 days, the reduction in organoids and enlarged size in the control formulation suggest a reduction in organoid yield due to organoid fusion.
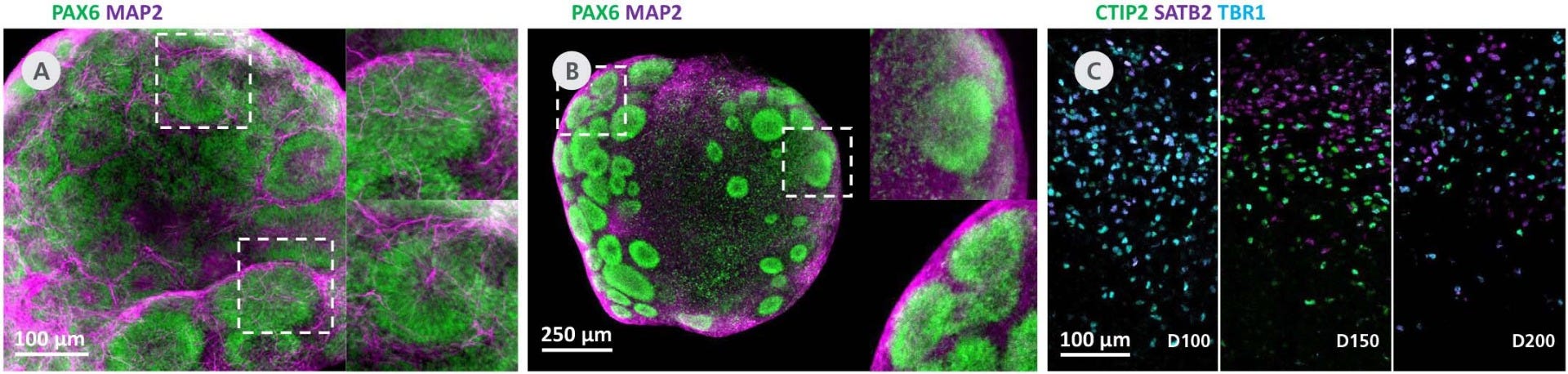
Figure 4. STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoids Exhibit Cortical Layering and Brain-Region-Specific Marker Expression as They Mature
(A) Day 25 dorsal forebrain organoids display multiple cortical-like regions marked by radialized PAX6+ cells surrounded by MAP2 neurons. (B) Day 50 dorsal forebrain organoids continue to display multiple cortical-like regions marked by PAX6 (green) and MAP2 (magenta). (C) Dorsal forebrain organoids cultured for 100 - 200 days show increasing separation of deep-layer neurons (CTIP2, green; TBR1, cyan) from upper-layer neurons (SATB2, magenta).
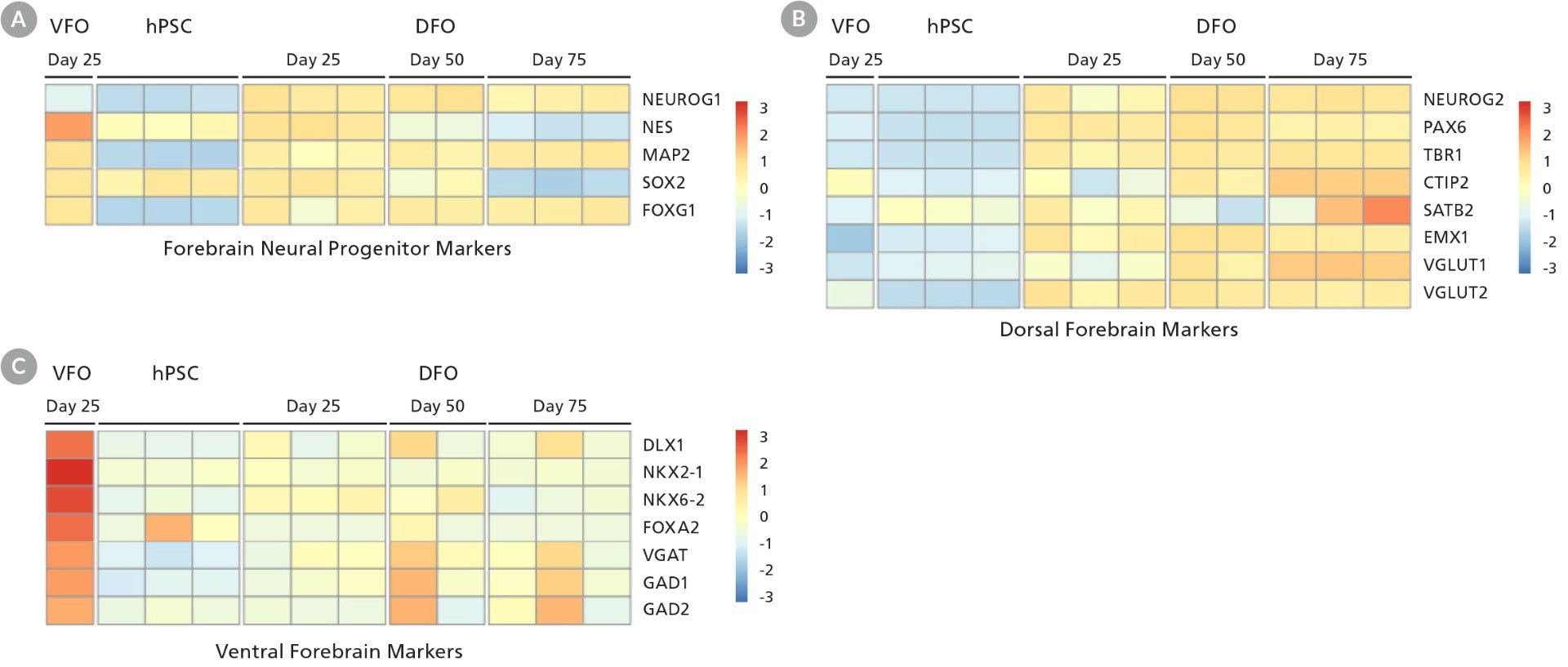
Figure 5. Neural Organoids Generated with STEMdiff™ Dorsal and Ventral Forebrain Organoid Kits Express Key Markers of Brain-Region-Specific Patterning
RNA from single organoids was harvested at a series of time points and subsequently assayed using bulk RNA-seq (1 data column = 1 organoid). (A) Heat map of select genes shows that both dorsal forebrain organoids (DFO) and ventral forebrain organoids (VFO) express the forebrain-specific marker FOXG1 while showing a shift from neural progenitor fates to neuronal cell types. (B) DFO express increasing levels of cortex- and glutaminergic neuron-specific genes from day 25 to 75. (C) Day 25 VFO exhibit high expression of markers of the medial ganglionic eminence and of GABAergic neurons. Heat map scale quantifies gene expression across each row with a normalized z-score for each gene.
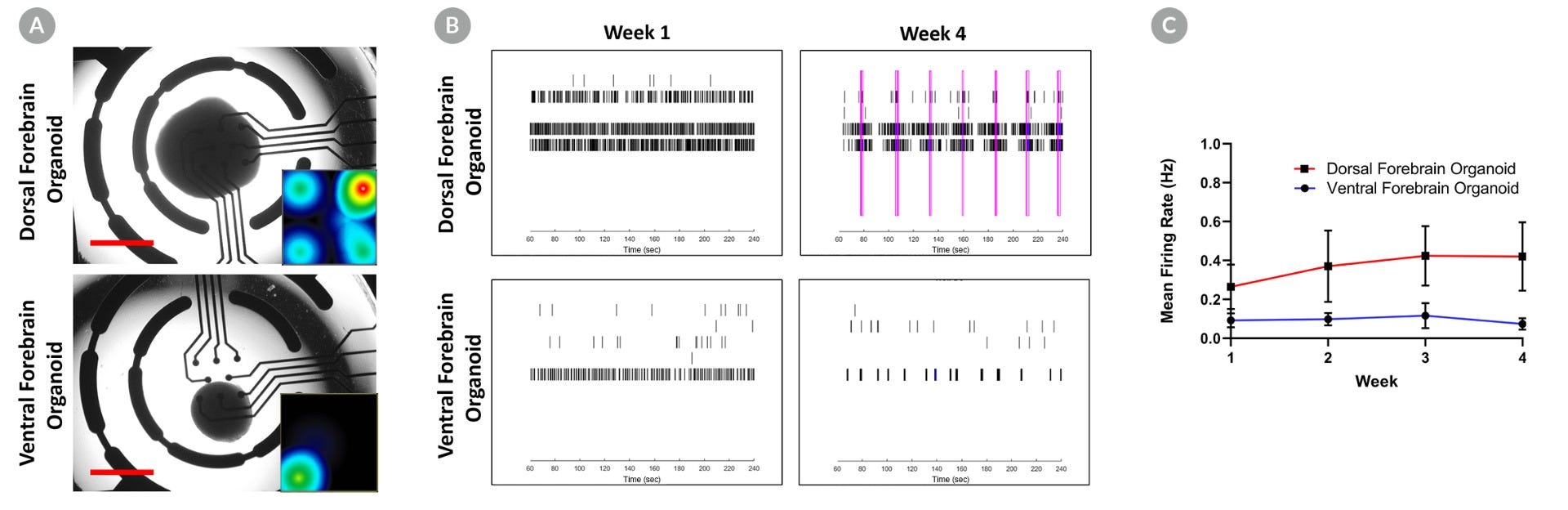
Figure 6. Dorsal Forebrain Organoids, Not Ventral Forebrain Organoids, Display Early Network Bursting Activity
Day 50 dorsal and ventral forebrain organoids were plated on a microelectrode array (MEA; CytoView MEA 96, Axion Biosystems) coated with 0.1% polyethyleneimine in borate buffer and 20 µg/mL CellAdhere™ Laminin-521. Activity from 8 electrodes per well was recorded once per week for 4 weeks using a Maestro MEA system (Axion Biosystems). (A) Representative bright field image of dorsal and ventral forebrain organoids on the MEA. Insets show representative spike rate heat maps for the corresponding well (red = 12 spikes/sec). Scale bar = 1 mm. (B) Raster plots of spike activity show increasing network bursting (pink lines) for dorsal forebrain organoids between week 1 and week 4, whereas no network bursting is observed in the ventral forebrain organoid (lower panels) over the same time period. (C) Mean firing rate (average ± SEM; 3 - 6 organoids per time point) increases for dorsal forebrain organoids but not ventral forebrain organoids over 4 weeks of measurements.
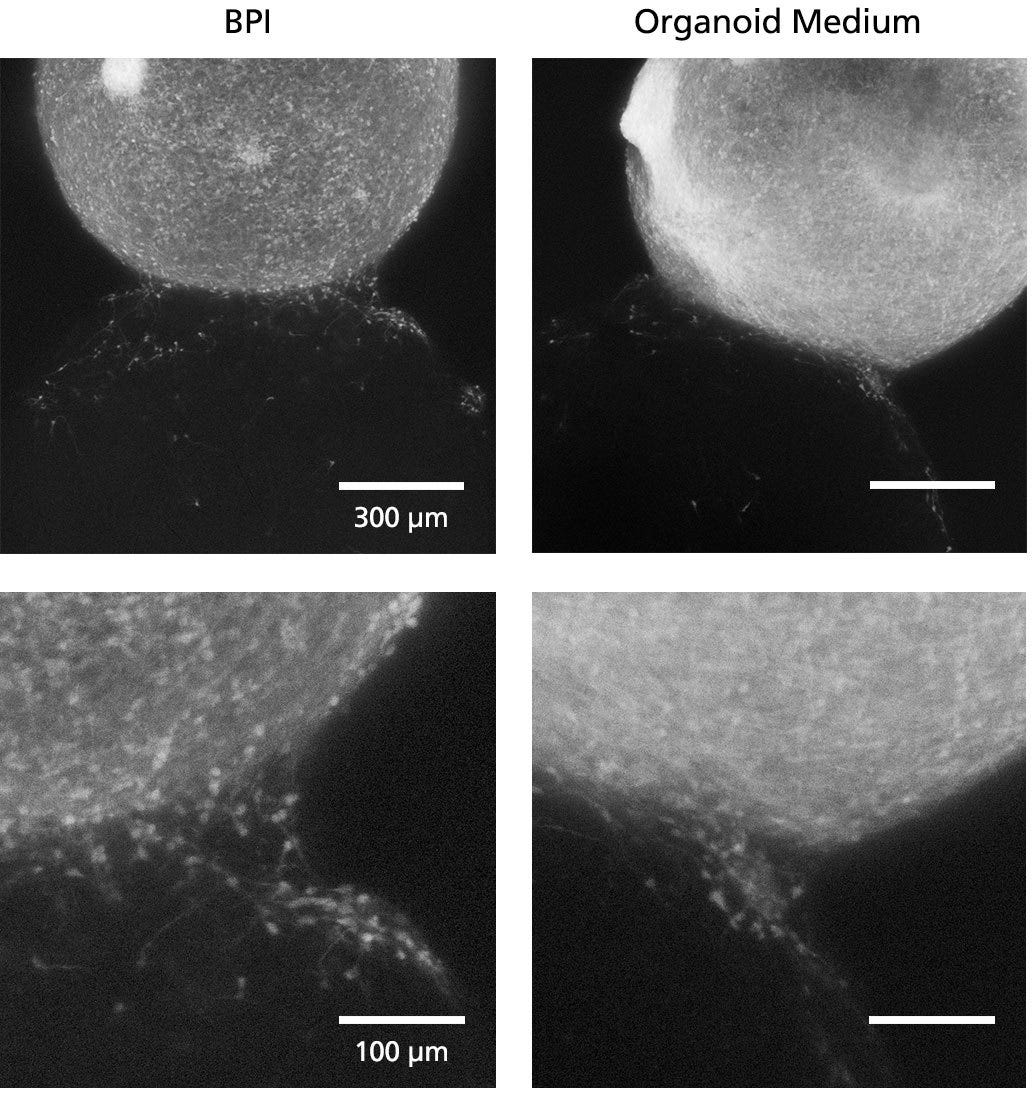
Figure 7. Fluorescent Imaging in BrainPhys™ Imaging Optimized Medium Improves Signal-to-Background Ratios of 3D Neural Cultures
GFP-labeled ventral forebrain organoids were co-cultured and merged with unlabeled dorsal forebrain organoids for one week prior to live imaging in Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Medium from STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit (right) or BrainPhys™ Imaging Optimized Medium (BPI, left). Interneuron migration can be visualized more clearly in BPI. Scale bar top panels = 300μm; scale bar bottom = 100μm. Adapted from Zabolocki et al. 2020, Nature Communications, available under a Creative Commons 4.0 License. For experimental details on generating AssemBloids™ from dorsal and ventral forebrain organoid co-cultures, see the protocol in our Methods Library.
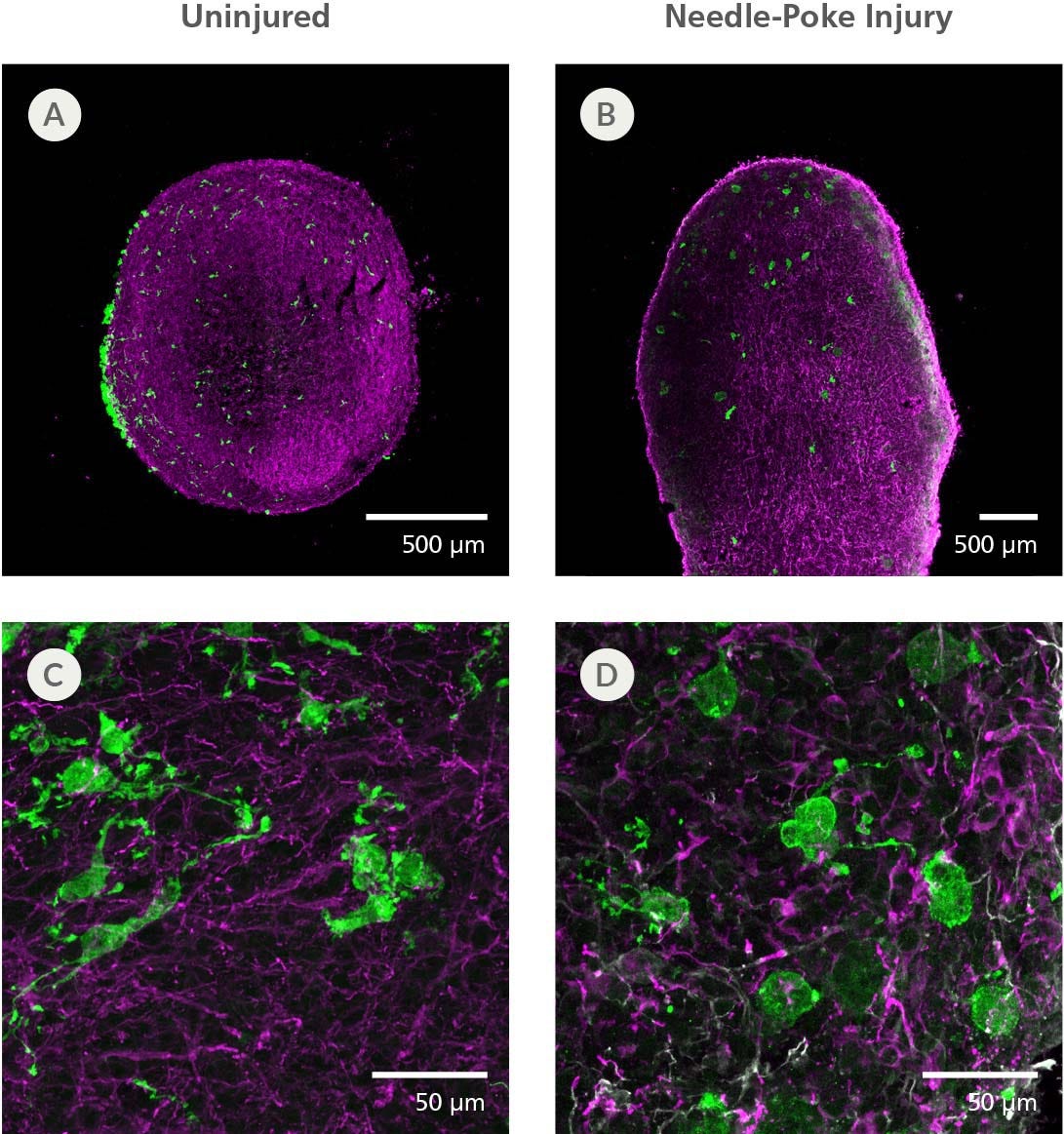
Figure 8. hPSC-Derived Microglia Incorporate into Brain Organoids After 10 Days and Display an Activated Morphology upon Injury
(A, C) Representative microglia and brain organoid co-cultures after 10 days, sectioned and stained with IBA1 for microglia (green) and MAP2 for neurons (magenta). The microglia integrate among the neurons and display an unactivated morphology with extended processes. (B, D) The microglia display an activated amoeboid morphology upon injury as shown by IBA1 staining.

Figure 9. Neural Organoids Generated with STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit Contain Dorsal Cell Populations
Guided dorsal forebrain organoids were generated from H9 ESCs using STEMdiff™ Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Differentiation Kit. scRNA-seq gene expression data captures the cellular diversity of these neural organoids which can be further explored using the Single Cell RNA Sequencing Data Visualization Tool for Neural Organoids. At Day 50, the organoids were dissociated into a single-cell suspension. The library was prepared using Chromium Single Cell 3ʹ v1 protocol with Feature Barcoding technology (10x Genomics) following surface protein staining with TotalSeq™–B (BioLegend). The barcoded processing, gene counting and aggregation were done using the Cell Ranger software v3.1.0. Further processing and demultiplexing was done with Seurat v4.1.1. The data have been made publicly available on GEO: GSE218457. ESC = embryonic stem cell
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Species | Human |
|---|---|
| Formulation Category | Serum-Free |
提升神经元功能的无血清基础培养基
用于人脑类器官建立与成熟的培养基试剂盒
用于从人多能干细胞高效生成腹侧前脑神经类器官的细胞培养基试剂盒
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。