产品号 #100-0214_C
细胞培养基进一步分化人肠道类器官在三维,或作为单层/气液界面培养
Cell culture medium for establishment and maintenance of human intestinal organoids
cGMP, enzyme-free cell dissociation reagent
Polystyrene plate with lid and polyester membrane inserts for cell culture that feed basolaterally
RHO/ROCK pathway inhibitor; Inhibits ROCK1 and ROCK2
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
Organoids have truly expanded the limits of what's possible for in vitro studies of the intestinal epithelium. By providing optimized culture media and robust, approachable protocols, we are making these technologies more accessible to researchers.

inteticult™类器官分化培养基(人)是一种完整的培养基,支持在三维(3D)或二维(单层或气液界面(ALI)培养中进一步分化肠道类器官。起始培养物可以是来源于人肠隐窝的类肠道器官,也可以是与interticult™类器官生长培养基(人类;目录# 06010)。
使用肠系膜™类器官分化培养基(人)生成的肠道培养物含有生理相关比例的分化细胞和干细胞群,概括了隐窝绒毛轴的多样性。与传统细胞系相比,肠单层细胞系表现出更大的屏障完整性,表达更高水平的关键分化标志物,并且具有更能代表体内肠道的形态学。
肠道类器官培养的应用包括研究肠上皮的发育和功能,模拟肠道疾病,化合物筛选和再生治疗方法。肠道单层培养物和ALI培养物特别适合于渗透性测定和传染病研究,因为它们易于接触到根尖表面。该试剂盒需要inteticult™类器官生长培养基(人;目录#06010),用于肠道类器官分化前的起始和扩张。
学习如何培养人类肠道类器官按需肠道疗程或浏览我们的常见问题(FAQs)关于使用inteticult™的类器官工作流程。此外,下载我们详细的电子书经过验证的肠道类器官培养方案:开始使用inteticult™肠道类器官方案的精选集。
如果您打算将本产品用于商业用途,请与HUB Organoids B.V.联系www.huborganoids.nl申请商业用途许可证或澄清与HUB Organoids B.V.许可有关的信息。
Subtype
Specialized Media
Cell Type
Intestinal Cells
Species
Human
Application
Cell Culture, Differentiation, Expansion, Maintenance, Organoid Culture
Brand
IntestiCult
Area of Interest
Disease Modeling, Drug Discovery and Toxicity Testing, Epithelial Cell Biology, Stem Cell Biology
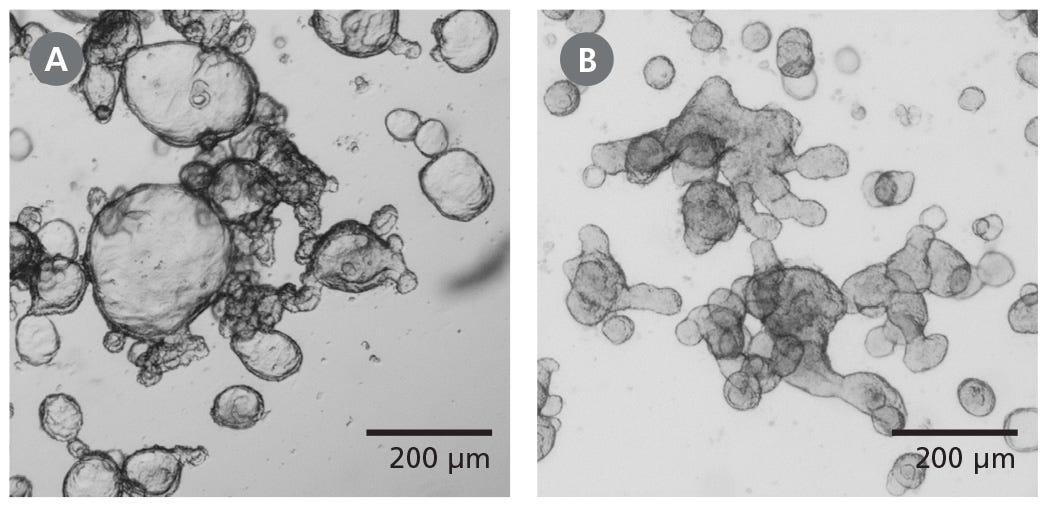
Figure 1. Differentiated Human Intestinal Organoids Display a Budded Morphology
(A) Organoids grown in IntestiCult™ OGM are primarily cystic. (B) When switched to IntestiCult™ ODM, organoids develop a thickened epithelium with a pronounced, budded morphology indicative of a more differentiated state. Organoids were imaged on day 5 of expansion or differentiation respectively.
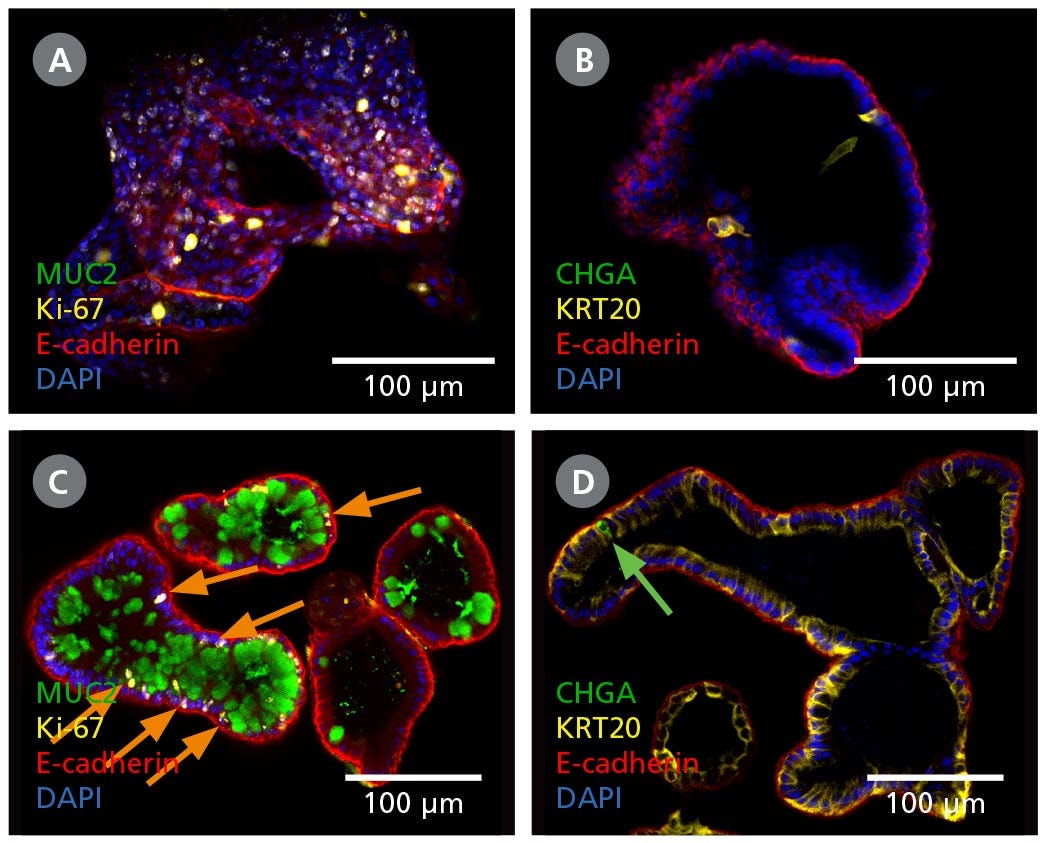
Figure 2. Intestinal Organoids Contain a Higher Proportion of Mature Cell Types Following Differentiation in IntestiCult™ ODM
(A, B) Organoids grown in IntestiCult™ OGM are enriched for Ki-67+ proliferative cells (A), while containing few differentiated cell types such as goblet cells (MUC2, A), enterocytes (KRT20, B), and enteroendocrine cells (CHGA, B). (C, D) When switched to IntestiCult™ ODM, organoids contain a small number of Ki-67+ proliferative cells (C, arrows), with more physiological proportions of goblet cells (MUC2, C), enterocytes (KRT20, D), and chromogranin A- (CHGA-)positive enteroendocrine cells (D, arrow).
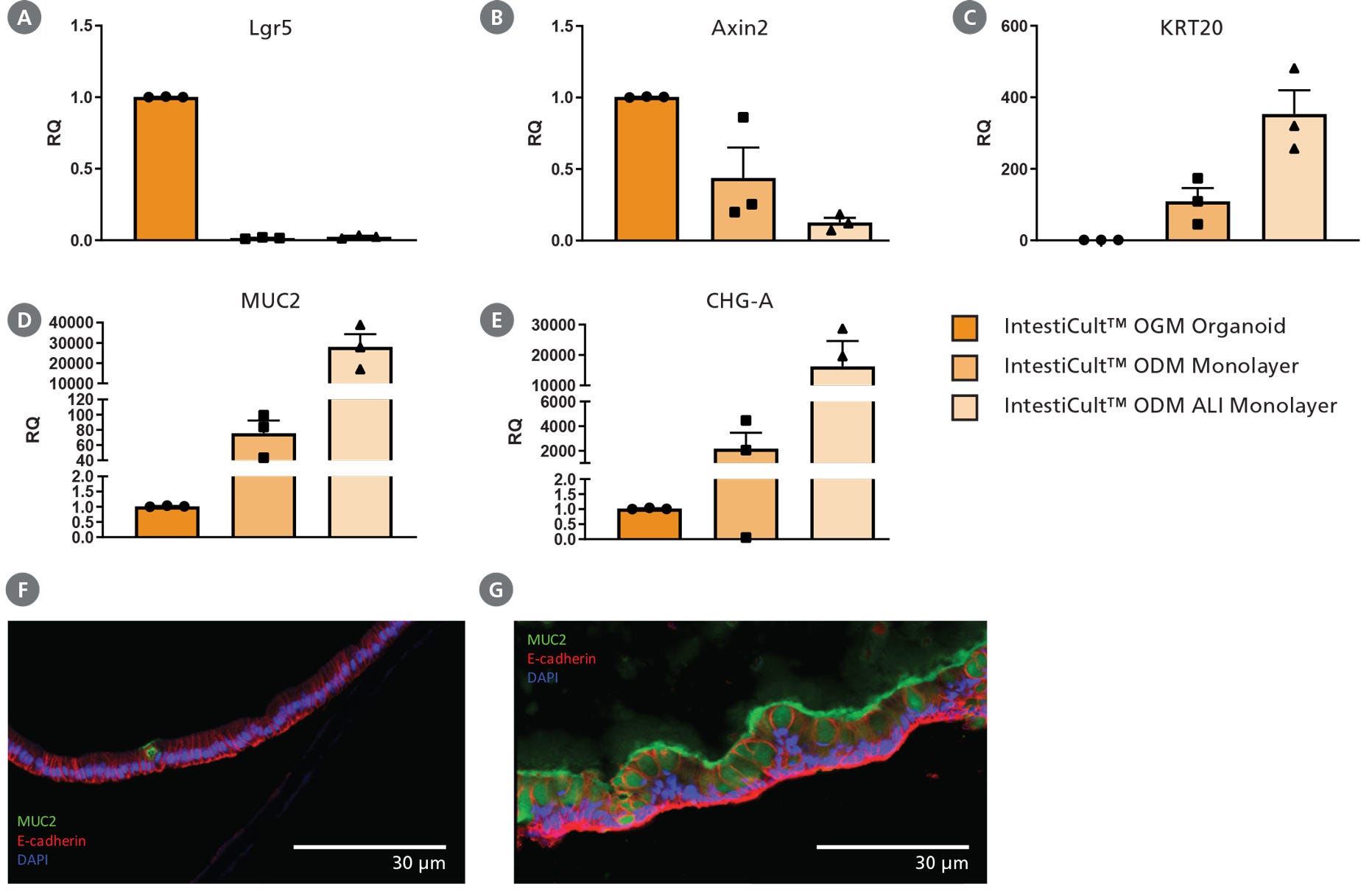
Figure 3. Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelium at the Air-Liquid Interface (ALI) Using IntestiCult™ ODM
(A – E) Growing organoid-derived monolayers as ALI cultures drives further differentiation of intestinal epithelial cultures as seen by changes in gene expression measured by RT-qPCR. Relative quantification (RQ) for each marker is shown relative to actB and TBP housekeeping genes and normalized with respect to undifferentiated organoids grown in IntestiCult OGM (Human). Progenitor markers (A) Lgr5 and (B) Axin2 are significantly reduced in both submerged monolayers and ALI cultures, while markers of enterocytes (KRT20, C), goblet cells (MUC2, D), and enteroendocrine cells (CHGA, E) are significantly increased. Further reduction in Axin2 is seen in ALI monolayers with an increase in expression of KRT20, MUC2, and CHGA. (F, G) Comparing cross-sections of organoid monolayers grown in IntestiCult™ ODM as (F) submerged culture or (G) at the ALI shows further differentiation of the intestinal epithelium with an increased proportion of goblet cells and extracellular mucus (MUC2, green).
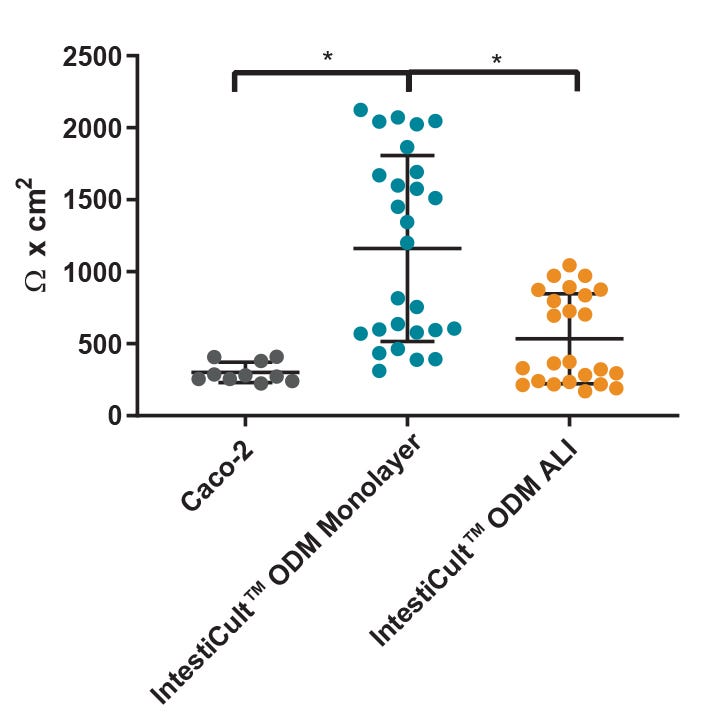
Figure 4. Differentiated Organoid-Derived Monolayers and ALI Cultures Display More Physiological Trans-Epithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) than Caco-2 Cells
Differentiated organoid-derived monolayers grown as a submerged monolayer (IntestiCult™ ODM Monolayer), or at the ALI (IntestiCult™ ODM ALI), show higher TEER values as compared to Caco-2 cultures.Organoid-derived monolayers grown at the ALI show a loosening of tight junctions due to further differentiation of the brush border, and thus lower TEER values are observed. * p < 0.0001.
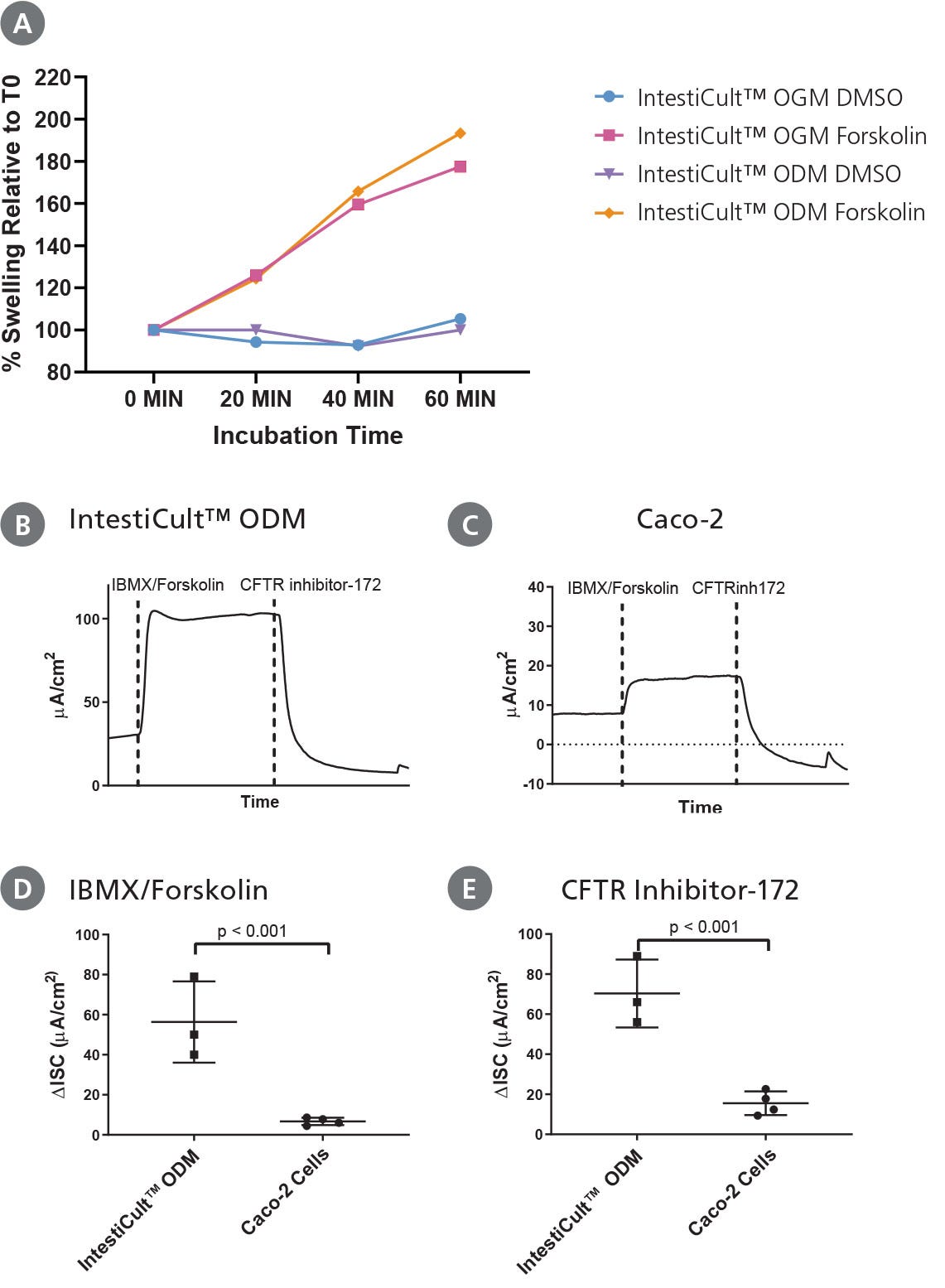
Figure 5. Differentiated Intestinal Organoids Provide a Suitable Model for Studying CFTR Response In Vitro
(A) Organoids differentiated further in IntestiCult™ ODM show a comparable degree of swelling when treated with forskolin as compared to organoids grown in IntestiCult™ OGM, demonstrating suitability for use in forskolin-induced swelling assays. (B – E) Ussing chamber analysis of submerged (B) organoid-derived monolayers and (C) Caco-2 cultures demonstrate increased sensitivity of organoid-derived monolayers to CFTR activation and inhibition by IBMX/Forskolin and CFTR Inhibitor-172 respectively. (D, E) Analysis of CFTR modulation by IBMX/Forskolin and CFTR Inhibitor-172 show significantly greater (D) activation and (E) inhibition of CFTR activity in organoid-derived monolayers as compared to Caco-2 cultures (p < 0.001 for both).

Figure 6. The MIMETAS OrganoReady® Colon Organoid Platform Uses IntestiCult™ to Create an Advanced Physiologically Relevant Model for Gastrointestinal Toxicity Testing and Barrier Integrity
(A) The OrganoReady® plate highlighting the microfluidic compartments.
(B) Schematic of the OrganoReady® microfluidic compartments where columns 1, 2, and 3 house the medium, a collagen-1 matrix, and the colon organoid tubule, respectively.
(C) Immunofluorescence staining of the colon organoid tubule confirms an adult tissue phenotype with the presence of goblet cells (Muc2), enterocytes (Occludin), and stem cells (Sox9). The 3D-lumenized structure provides apical (Ezrin) and basolateral (Integrin-β4) access to the polarized epithelium. Additionally, the organoid tubules show polarized and modulatable activity of expression of P-glycoprotein (Pgp).
(D) The OrganoReady® Colon Organoid platform supports toxicity testing, as demonstrated by dose-dependent measurements of TEER, LDH, and ATP following exposure to Afatinib (n = 4, N = 2). After 72 hrs of exposure, a dose dependent decrease in TEER, cytotoxicity, and cell viability was observed. For more information, please visit mimetas.com/en/organoready-organoid/.
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Species | Human |
|---|
酶解细胞试剂
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium/营养型火腿混合物F-12 (DMEM/F-12)与15 mM HEPES缓冲液
Dulbecco的磷酸盐缓冲盐水,不含钙和镁
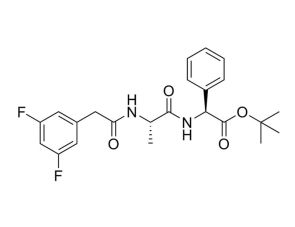
Notch 通路抑制剂;抑制 γ-分泌酶
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。