产品号 #100-0383_C
用于人肝脏类器官分化的培养基试剂盒
Culture medium for long-term expansion and maintenance of human liver organoids

Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium/Nutrient Ham's Mixture F-12 (DMEM/F-12) with 15 mM HEPES buffer
Glucocorticoid pathway activator; Activates glucocorticoid receptor
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
使用 HepatiCult™ 类器官分化培养基(ODM)(人源)可稳定生成具有肝脏功能性的成熟人源肝脏类器官。该培养基包含支持新鲜或冻存人肝组织来源的肝脏类器官高效分化所需的所有组分。
HepatiCult™ ODM 既可单独购买,也可作为 HepatiCult™ 类器官试剂盒(人源)的一部分使用,适用于对 HepatiCult™ 类器官起始培养基(人源)中生成的类器官和/或在 HepatiCult™ 类器官生长培养基(人源)中扩增的类器官进行分化培养。经 HepatiCult™ ODM 分化的类器官表达肝细胞标志物(ALB、CYP3A4、MRP4),与未分化类器官相比,其白蛋白分泌水平与 CYP3A4 活性显著上调。这些类器官可适配多种培养方案,包括悬浮培养体系和高通量检测。
有关 HepatiCult™ 类器官培养方案的更多信息,请参阅技术手册与教育资料。
如果您打算将此产品用于商业目的,请通过www.huborganoids.nl联系HUB以获得商业使用许可或有关HUB许可的说明。
Subtype
Specialized Media
Cell Type
Hepatic Cells
Species
Human
Application
Organoid Culture
Brand
HepatiCult
Area of Interest
Disease Modeling, Drug Discovery and Toxicity Testing, Epithelial Cell Biology, Organoids, Stem Cell Biology
Formulation Category
Serum-Free
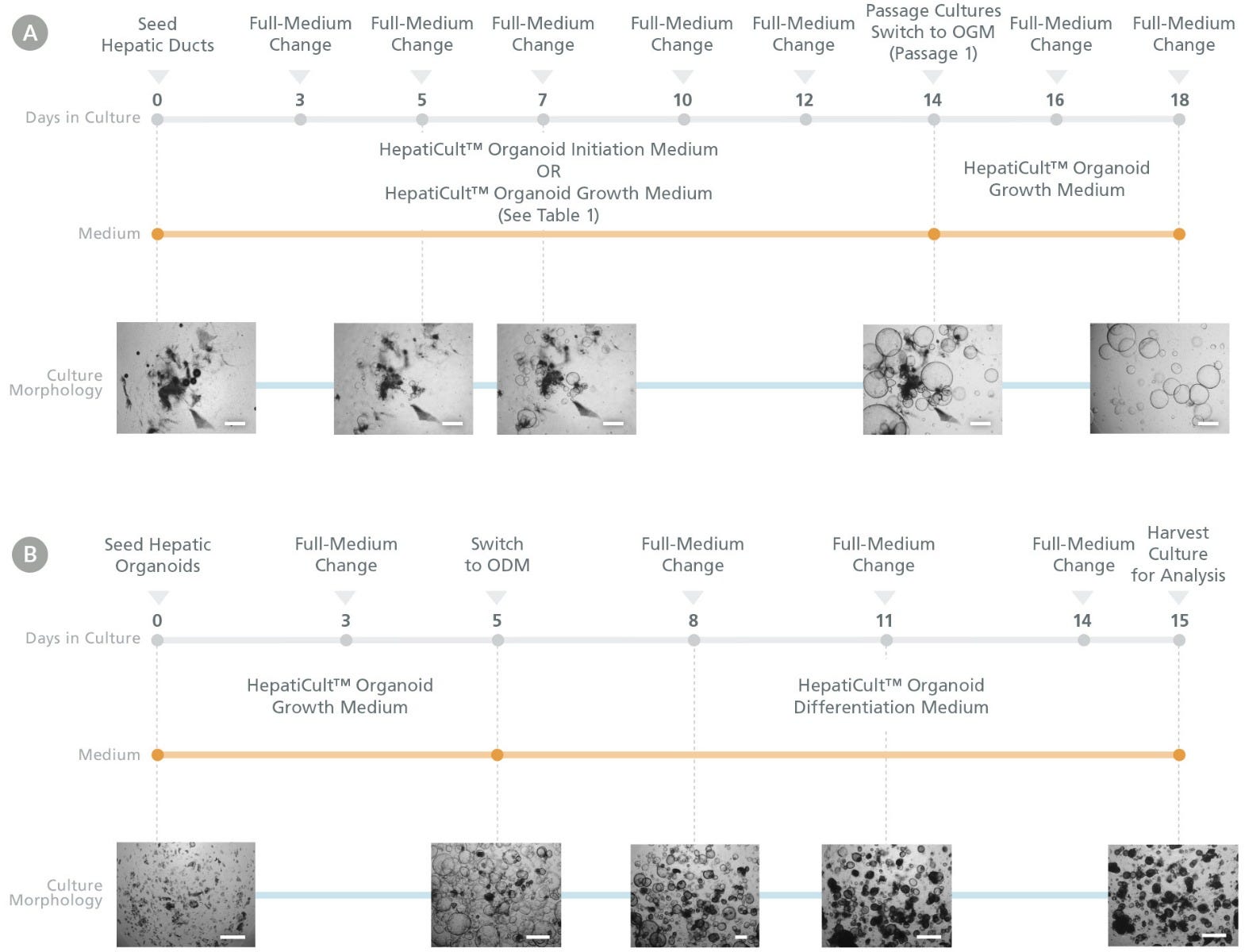
Figure 1. HepatiCult™ Organoid Kit (Human) Enables Liver Organoid Initiation, Expansion, and Differentiation
Human liver organoids can be grown from normal human liver tissue-derived hepatic ducts using the HepatiCult™ Organoid Kit (Human). (A) Cultures are established in HepatiCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM; Human) or HepatiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (OGM; Human) (see Table 1 below) and subsequently passaged in HepatiCult™ OGM for expansion. (B) After passaging 2-3 times in HepatiCult™ OGM, cultures can be switched to HepatiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium (ODM; Human) to differentiate organoids towards more mature hepatic cell types. Refer to the Product Manual (Document #10000008301) for full culturing protocols.
Table 1. Product Recommendations for Liver Organoid Initiation, Expansion, and Differentiation
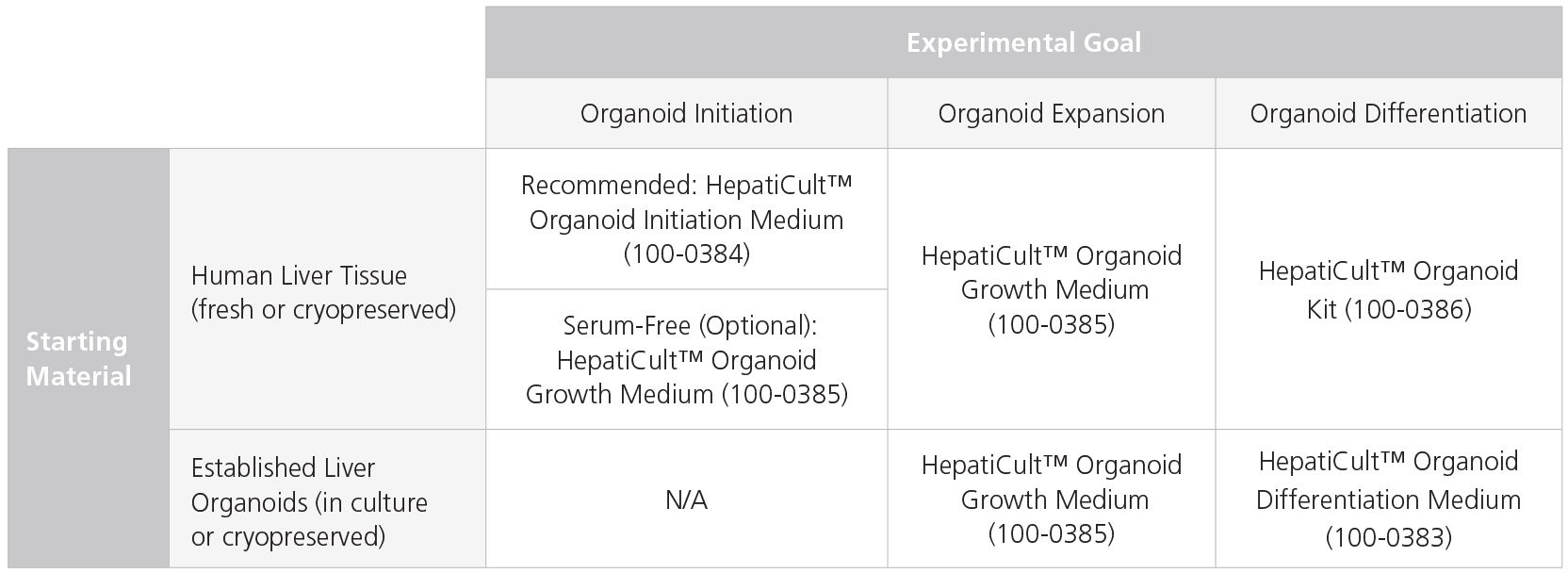
The recommended configuration of the HepatiCult™ Organoid Kit (Human) may differ based on starting material and experimental goals. When establishing liver organoid cultures from human liver tissue, HepatiCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM; Human) is recommended for efficient organoid initiation (see Figure 2 below). The expansion of already established organoids (fresh in culture or cryopreserved) is supported by HepatiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (OGM; Human). These organoids should be maintained for 2-3 passages before further differentiation using HepatiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium (ODM). Refer to the Product Manual (Document #10000008301) for full culturing protocols.
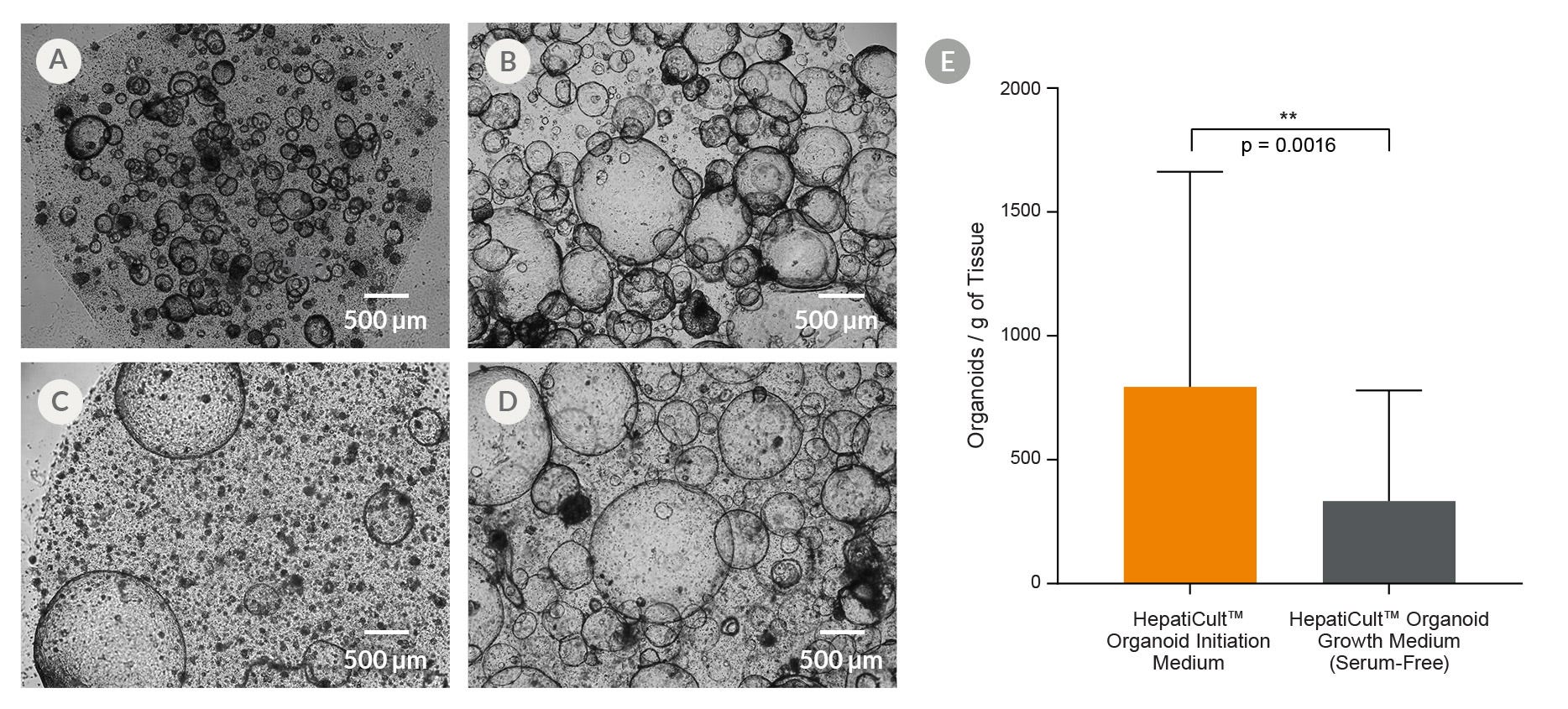
Figure 2. HepatiCult™ Organoid Kit (Human) Provides Efficient Organoid Initiation From Human Liver Tissue
(A) Organoid cultures were initiated in HepatiCult™ OIM, and then (B) passaged into HepatiCult™ OGM. For serum-free culture conditions, organoid cultures were both, (C) initiated in and (D) passaged in HepatiCult™ OGM. Culture images shown are from (A, C) day 15 following initiation, and (B, D) on day 8 of the first passage. (E) Quantification of organoid initiation efficiency shows a significantly higher organoid yield in HepatiCult™ OIM per gram of human liver tissue (mean ± SD; n=14).
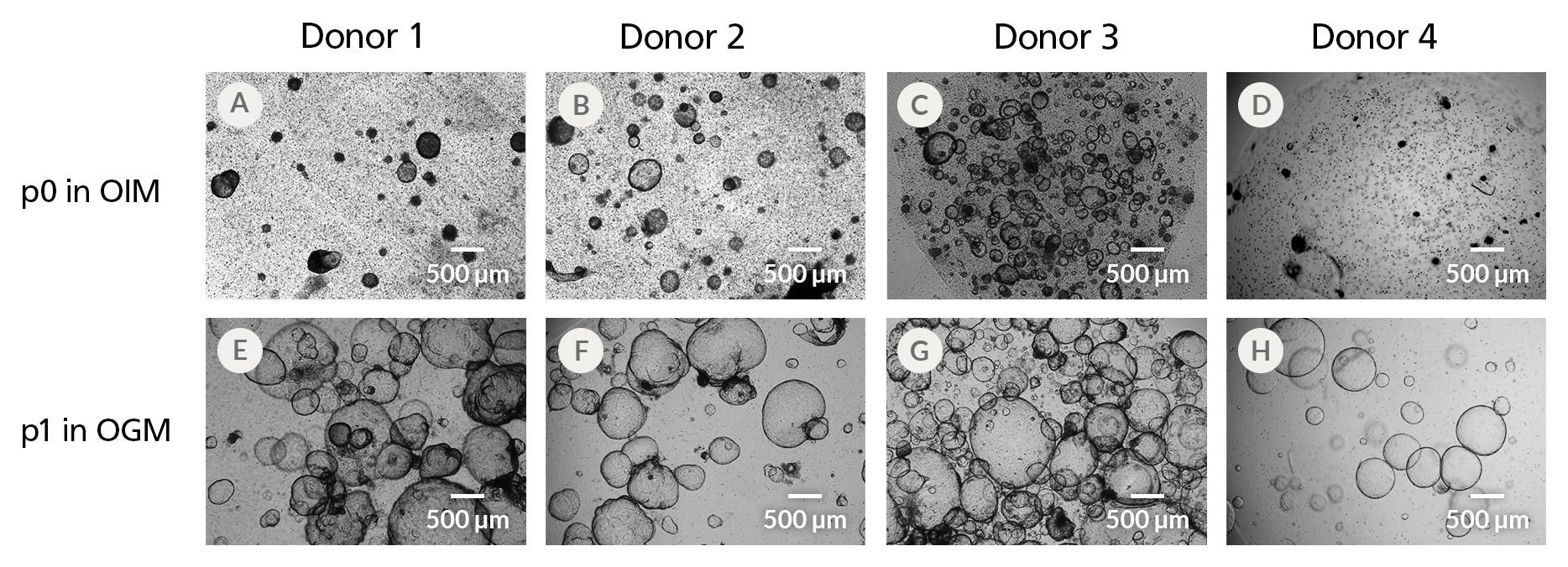
Figure 3. HepatiCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) Supports Robust Organoid Establishment Across Multiple Liver Tissue Donor Samples
Organoids initiated from 4 donor tissue samples (A-D) exhibit morphological heterogeneity 15 days after initiation. All initiated cultures were subsequently expanded in HepatiCult™ OGM using a 1:1 passaging ratio (E-H), yielding healthy organoids at the end of the first passage.
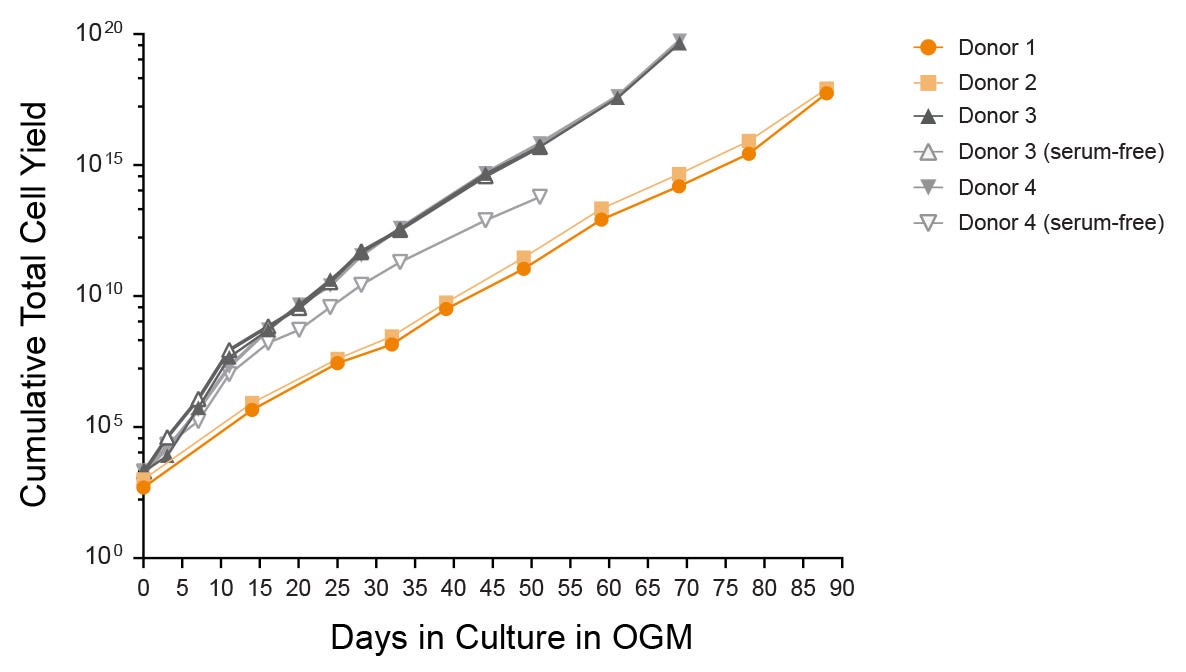
Figure 4. Expansion of Organoid Cultures in HepatiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium
Hepatic organoids show efficient growth in HepatiCult™ OGM across multiple donors and passages with potential for indefinite culture. Organoids initiated using the serum-free workflow exhibited comparable growth rates when expanded in HepatiCult™ OGM (open markers).
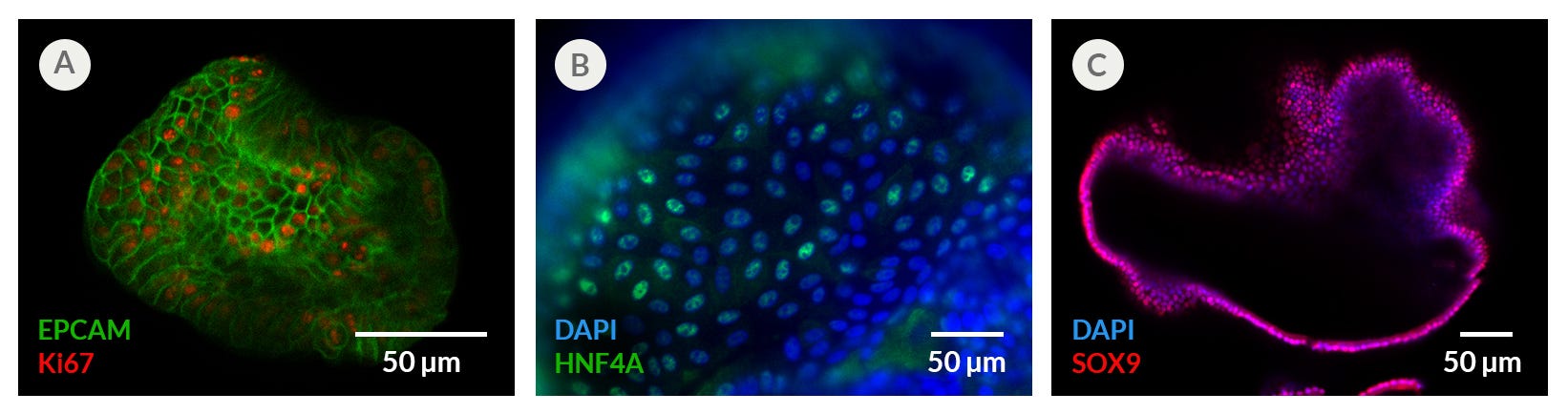
Figure 5. Proliferating Hepatic Organoids Display Characteristics of Hepatic Progenitors
Human liver organoids grown in HepatiCult™ OGM display characteristics of proliferating hepatic progenitors observed through immunocytochemistry staining of (A) KI67, (B) HNF4A and (C) SOX9. Proliferating hepatic organoids also display characteristics of the hepatic epithelium including expression of (A) EPCAM. (B, C) Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI.
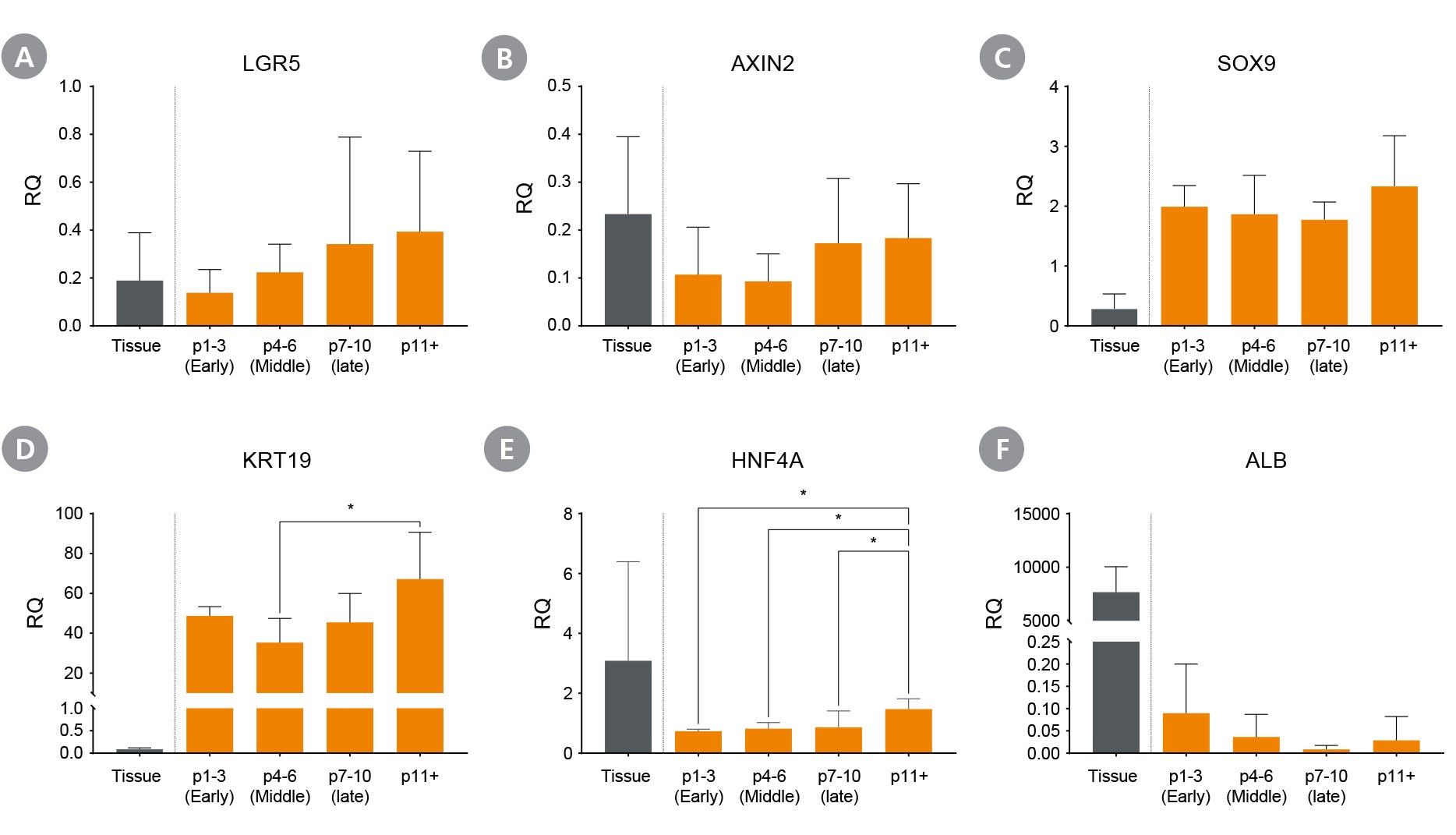
Figure 6. Proliferating Hepatic Organoids Maintain Genetic Expression Across Multiple Passages
Liver organoids maintained in HepatiCult™ OGM express stem cell markers (A) LGR5 and (B) AXIN2, ductal markers (C) SOX9 and (D) KRT19, as well as hepatic marker (E) HNF4a and (F) Albumin (ALB) across multiple passages, with minimal albumin expression observed during culture in HepatiCult™ OGM. Expression levels were measured by qPCR and normalized to TBP and UBC housekeeping genes to quantify relative expression levels. (mean ± SD; n = 2-5 organoid lines), * p < 0.05.
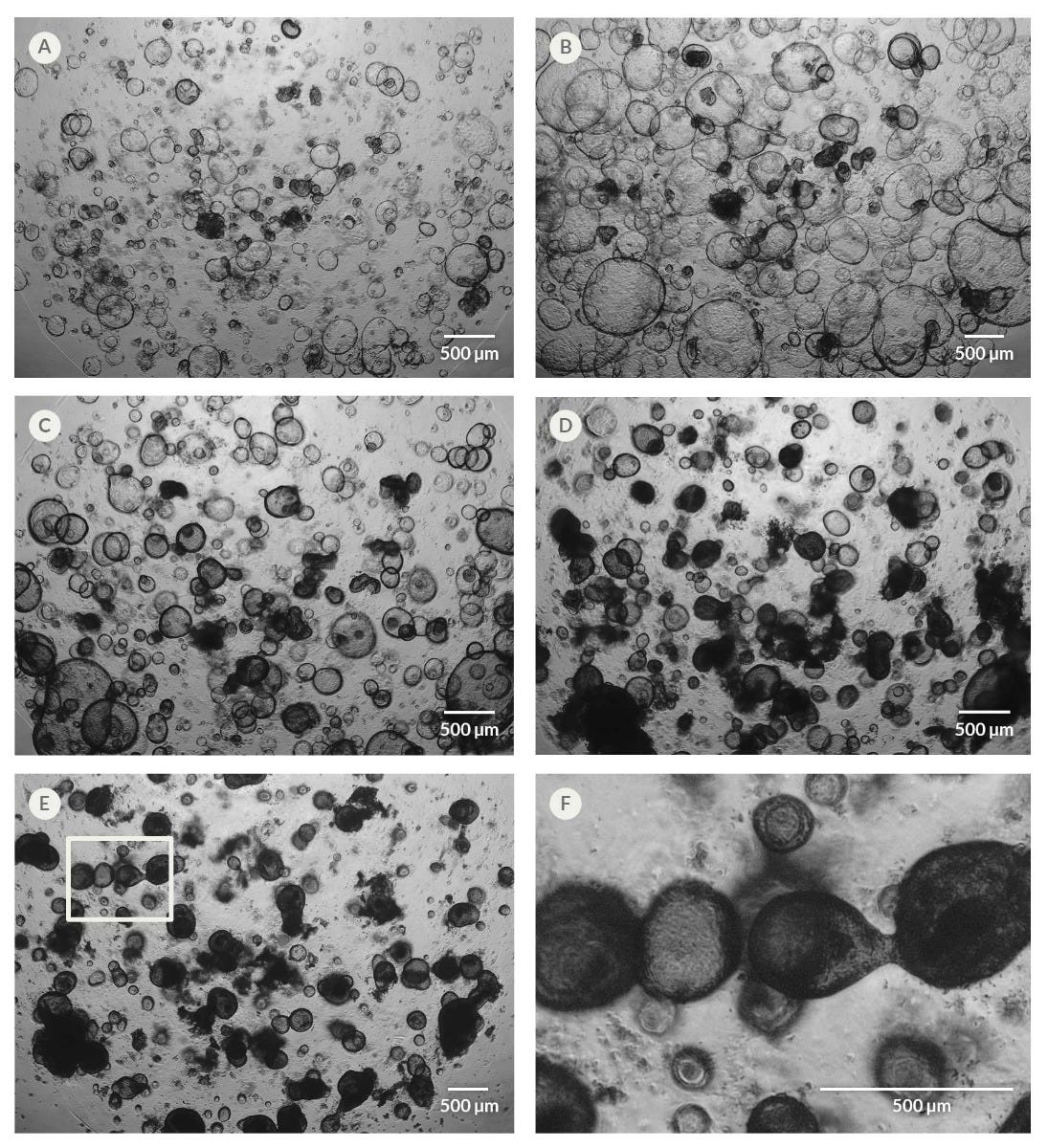
Figure 7. Organoid Differentiation Induces Changes in Organoid Morphology
Organoids exhibit a compact and dense morphology, often comprising thickened epithelia, upon switching cultures to HepatiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium (ODM). Shown are images of the same culture well over the course of the differentiation, including (A) day two of culture in HepatiCult™ OGM, (B) day five of culture, immediately after switching organoid cultures from HepatiCult™ OGM to HepatiCult™ ODM, (C) day seven of culture (two days after switching to ODM), (D) day ten of culture (five days after switching to ODM), and (E) day 15 of culture (ten days after switching to ODM). (F) Magnification of the rectangular section highlighted in (E).
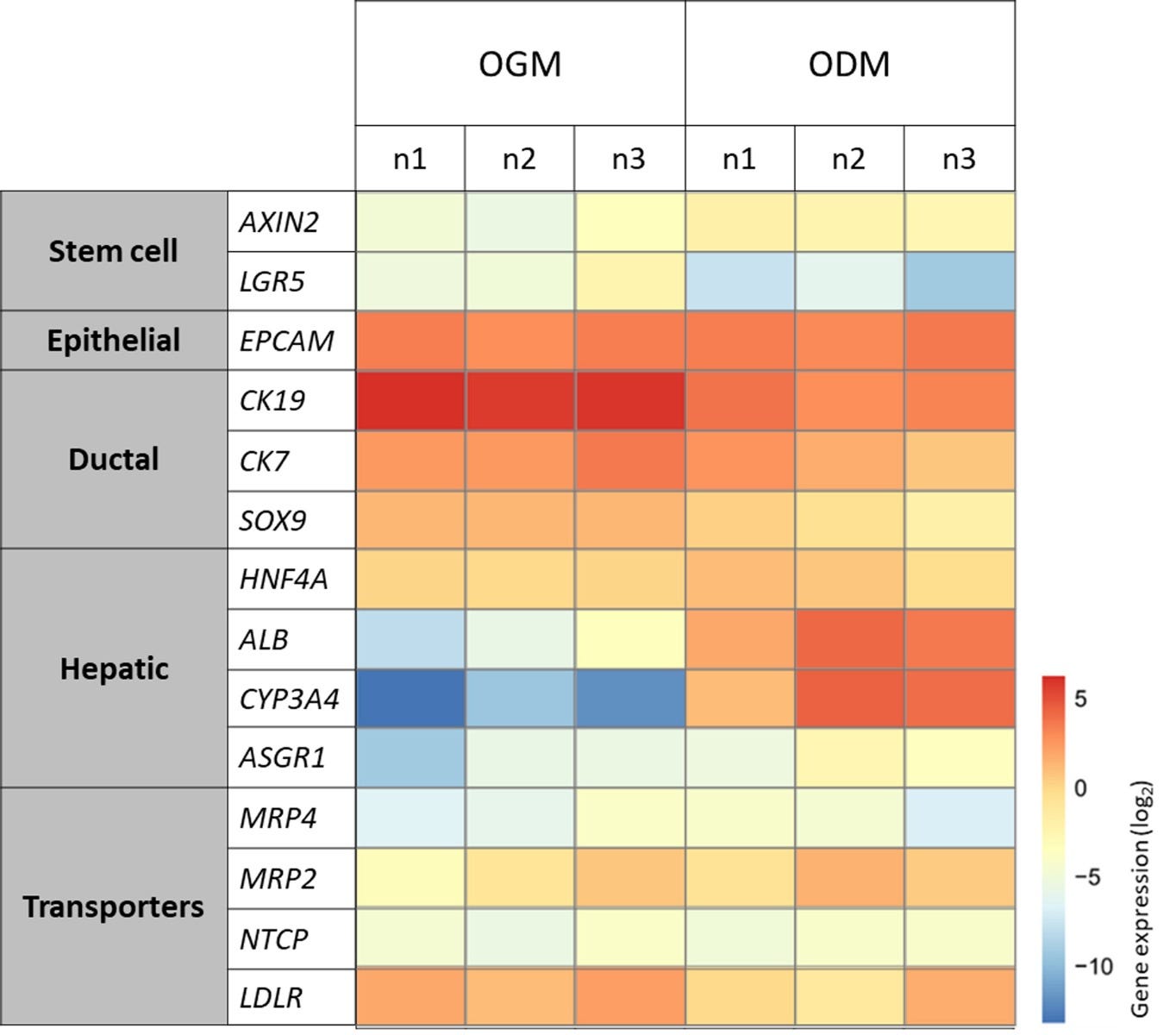
Figure 8. Differentiation of Hepatic Organoids in HepatiCult™ ODM Induces Changes in Gene Expression Consistent With Hepatic Maturation
Upon differentiation in HepatiCult™ ODM, liver organoids show changes in gene expression with a decrease in expression of stem cell marker LGR5, as well as of ductal markers CK19, CK7, and SOX9, and an increase in expression of hepatic markers HNF4A, ALB, CYP3A4, and ASGR1. Each replicate represents an individual donor sample analyzed by qPCR at passage 4 on day 8 in HepatiCult™ OGM and day 15 in HepatiCult™ ODM, showing relative gene expression levels normalized to TBP and UBC housekeeping genes.
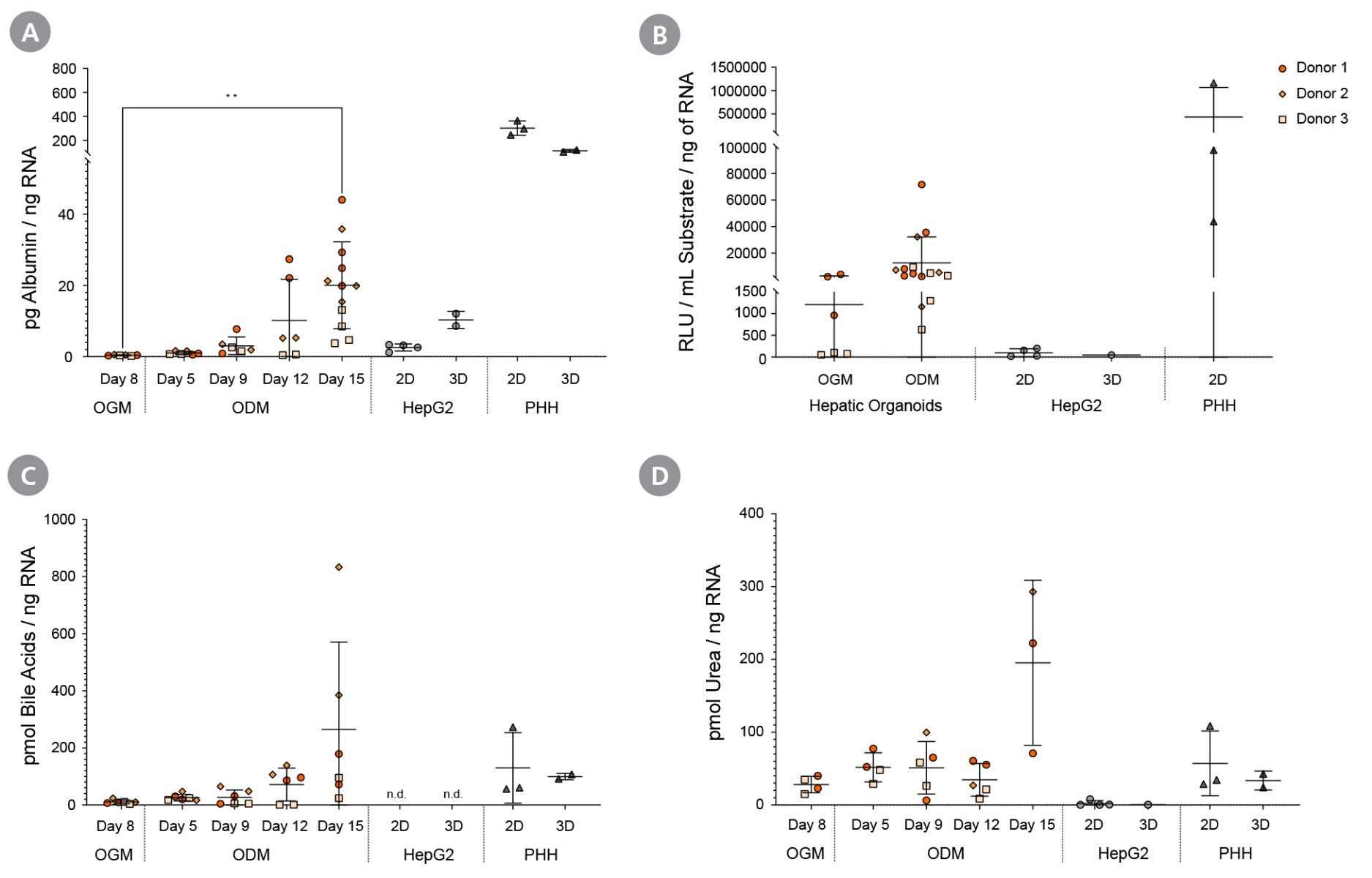
Figure 9. Differentiated Hepatic Organoids Demonstrate Functionality of Mature Hepatocytes
Upon differentiation in HepatiCult™ ODM, liver organoids were assayed for (A) albumin secretion, (B) CYP3A4 activity, (C) total bile acid production, and (D) urea production. Hepatic functionalities were compared to HepG2 cells and primary human hepatocytes (PHH), which were cultured in supplier-recommended media. Albumin secretion was detected using an ELISA kit (Abcam), total bile acid and urea production were analysed using colorimetric kits (Abcam), and CYP43A4 activity, referring to baseline activity without induction, was determined using the Luciferin-IPA kit (Promega). (mean ± SD; n = 3 organoid lines across 2 experiments, n = 2-3 technical replicates of HepG2 in 1 experiment, and n = 3 cryopreserved PHH donor samples in 1 experiment), * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
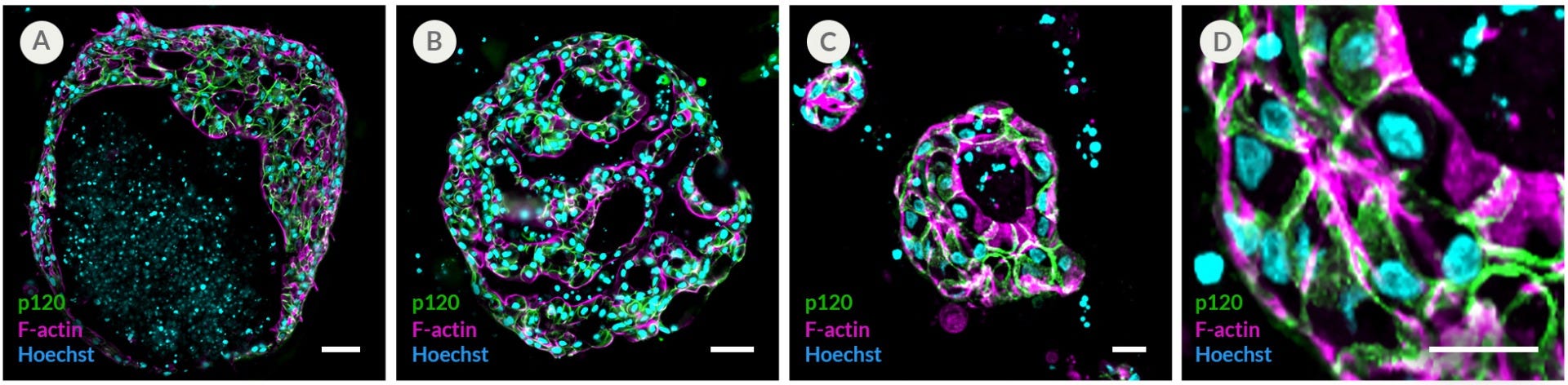
Figure 10. HepatiCult™ Organoid Kit Supports the Growth and Differentiation of Porcine Liver Organoids
Porcine liver organoids were established in HepatiCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium, and subsequently expanded for 4 passages in (A) HepatiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) and differentiated in (B, C) HepatiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium (Human). Organoids are stained with basolateral protein marker p120 (green), apical membrane and bile canaliculi marker F-Actin (purple), and nuclear dye Hoechst (blue). (D) Magnification of Panel C indicates bile canaliculi formation as seen through F-Actin staining. Scale bars = 50 μm. Data used with permission from Dr. Amy Engevik (Vanderbilt University Medical Center)
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Species | Human |
|---|---|
| Formulation Category | Serum-Free |
建立和维持小鼠肝祖类器官的细胞培养基
从人PSCs中产生肝细胞样细胞的无血清分化试剂盒
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。