产品号 #100-0900_C
用于将人胚胎干细胞(ES细胞)或诱导多能干细胞(iPS细胞)分化为巨核细胞和血小板。
用于将人胚胎干细胞(ES细胞)或诱导多能干细胞(iPS细胞)分化为巨核细胞和血小板。
STEMdiff™ 巨核细胞试剂盒专为在无血清、无饲养层的条件下,将人类胚胎干细胞(ES细胞)和诱导多能干细胞(iPS细胞)分化为具有多倍体、可释放血小板并表达 CD41a 和 CD42b 的巨核细胞而设计。本试剂盒采用一个简单的二维、为期17天的分化方案,包含两个阶段。
在前 12 天,将 STEMdiff™ 造血补充剂 A 和补充剂 MK1 添加到基础培养基中,以诱导细胞向巨核细胞倾向的造血祖细胞分化。在此阶段结束时,可从培养上清液中轻松收获造血祖细胞,并使用补充剂 MK2 和 StemSpan™ SFEM II 继续培养 5 天,使其进一步分化为成熟的巨核细胞。
在方案结束时(第17天),细胞通常可扩增至初始数量的约405倍±54倍(95% 置信区间),平均约有71%±3.3%(95% 置信区间)的细胞共表达CD41a和CD42b。
STEMdiff™ 巨核细胞试剂盒已针对在以下培养体系中维持的 ES/iPS 细胞进行了优化:mTeSR™1(目录号 85850)、mTeSR™ Plus(目录号 100-0276)或 TeSR™-AOF(目录号 100-0401)。
亚型
专用培养基
细胞类型
造血细胞,PSC衍生,造血干/祖细胞,巨核细胞
应用
分化
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,干细胞生物学,细胞治疗开发
制剂类别
无血清

Figure 1. Megakaryocyte Differentiation Protocol
The 17-day protocol includes two main stages: a 12-day stage to differentiate human embryonic stem (hES) or induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells into megakaryocyte-biased hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs), and a 5-day stage to further differentiate hES or hiPS cell-derived HPCs into mature megakaryocytes (MKs). On Day -1, hES or hiPS cells are plated as aggregates (100 - 200 μm diameter, ~100 cells per aggregate) at a density of 10 ‑ 20 aggregates/cm2 in mTeSR™1, mTeSR™ Plus, or TeSR™-AOF on Corning® Matrigel®-coated plates. After attaching overnight and confirming the number of adhered colonies is within 4 - 10 colonies/cm2, mesoderm induction is initiated by replacing TeSR™ medium with Medium A (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Supplement A). On Day 3, the medium is changed to Medium MK1 (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Supplement MK1) for endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition (EHT) and hematopoietic specification. During this phase, hES or hiPS cell-derived HPCs emerge from an adherent layer of endothelial cells and are released into suspension. On Day 12, HPCs in suspension are harvested and replated in Medium MK2 (StemSpan™ SFEM II + STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Supplement MK2) at a density of 1 - 3.5 x 105 cells/mL and cultured for 5 days to generate mature MKs.

Figure 2. hPSCs Differentiate to Megakaryocyte-Erythroid Progenitors During 12 Days of Culture
hES and hiPS cells were induced to differentiate to megakaryocyte-erythroid biased HPCs following the protocol described in Figure 1. On Day 12, cells were harvested from the supernatant and analyzed for expression of CD41a, CD42b, CD34, and GlyA by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and propidium iodide (PI) staining. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots for hES-derived (H9) cells on Day 12. The cells show high levels of CD41a and CD42b as well as of CD34 and GlyA expression, indicating that the protocol supports differentiation of hPSCs to megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors by Day 12. (B) Frequencies and numbers of CD41a+CD42b+ cells per input cell for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). The average frequency of viable CD41a+CD42b+ cells on Day 12 ranged between 33% and 62%. The average yield of CD41a+CD42b+ cells generated per input cell ranged between 72 and 174. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 for H1, n = 20 for H9, n = 19 for WLS-1C, n = 7 for STiPS-R038).

Figure 3. hPSC-Derived HPCs Efficiently Expand and Differentiate to CD41a+CD42b+ Megakaryocytes During an Additional 5 Days of Culture
hPSC-derived HPCs on Day 12 were cultured for 5 additional days in Medium MK2 to promote differentiation into mature MKs following the protocol described in Figure 1. Cells were harvested and analyzed for expression of CD41a, CD42b, CD34, and GlyA by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and PI staining. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots for hES-derived (H9) cells on Day 17. The cells showed high levels of CD41a and CD42b and low levels of GlyA and CD34 markers, indicating differentiation to megakaryocytes. (B) Frequencies and numbers of CD41a+CD42b+ MKs per input cell for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). The average frequency of viable CD41a+CD42b+ cells on day 17 ranged between 56% and 77%. The average yield of CD41a+CD42b+ MKs generated per input cell ranged between 223 and 425. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 12 for H1, n = 29 for H9, n = 27 for WLS-1C, n = 12 for STiPS-R038).

Figure 4. hPSC-Derived Megakaryocytes Generated Using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Are Polyploid
hPSC-derived MKs obtained using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit display mature and adult-like features: cellular enlargement and polyploidization. (A) A representative bright-field image taken on Day 17 showing large MKs derived from H1 cells (10X magnification). (B) Representative immunofluorescence images taken on Day 17 showing that CD41a+ MKs derived from H1 and WLS-1C cells are polyploid (20X and 63X magnification, respectively). The cells were formaldehyde-fixed and stained with a fluorescein-conjugated antibody against surface marker CD41a (green), and DAPI (blue). (C) A representative cytospin of MKs derived from H9 cells on Day 17 showing high ploidy (40X magnification, May-Grunwald Giemsa stain). (D) Representative flow cytometry histogram and scatter plot showing the DNA ploidy profile of ethanol-fixed MKs derived from H9 cells on Day 17. The DNA content was determined by the quantity of PI staining, with different peaks on the histogram representing 2N, 4N, and 8N+ cells. Ploidy analysis was done on gated CD41a+ cells. (E) Ploidy distribution of MKs generated from two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). The average ploidy distributions of CD41a+ cells on Day 17 were 66%, 24.5%, and 9.5% for 2N, 4N, and 8N+, respectively. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 6 for H1, n = 28 for H9, n = 19 for WLS-1C, n = 10 for STiPS-R038).
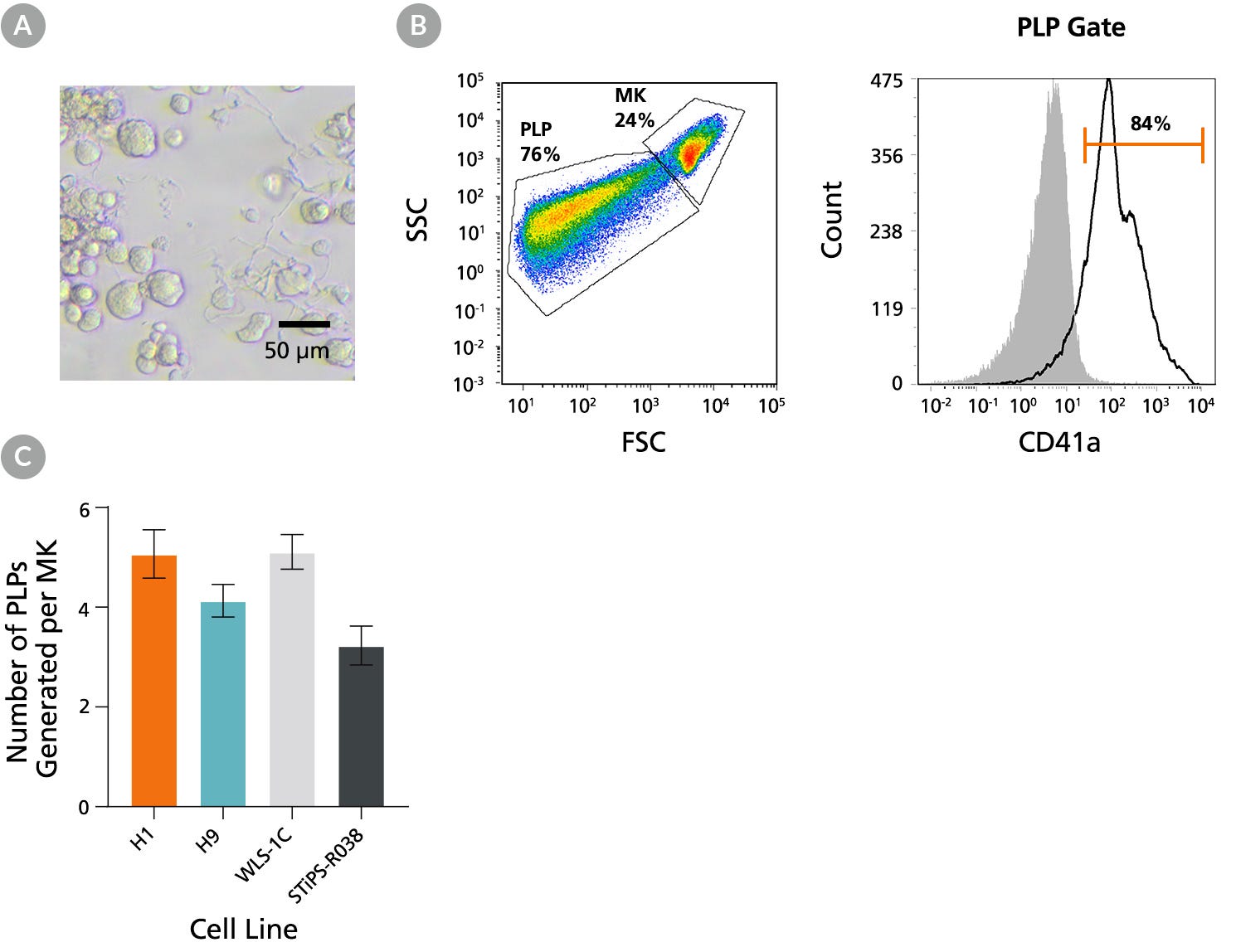
Figure 5. hPSC-Derived Megakaryocytes Generated Using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Yield Platelet-Like Particles
hPSC-derived MKs obtained using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit are capable of proplatelet formation to yield functional platelet-like particles (PLPs). (A) A representative bright-field image taken on Day 17 showing MKs derived from H1 cells formed proplatelets, (long cytoplasmic protrusions,10X magnification). (B) Representative flow cytometry forward/side scatter profile of MKs and PLPs and histogram of PLPs derived from H9 cells on Day 17. The PLP gate is based on control platelets (PLTs) prepared from fresh blood. Cells were also stained with antibodies against CD41a, CD45, and GlyA for PLP characterization and enumeration. PLPs showed a high level of CD41a expression (and no CD45 and GlyA expression, data not shown) as in control PLTs. Grey filled histogram represents CD41a Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) control. (C) Numbers of PLPs generated per MK on Day 17 for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). PLPs and MKs were enumerated based on the number of CD41a+CD45-GlyA- cells in the PLP gate and viable CD41a+ cells in the MK gate, respectively. The average yield of PLPs generated per MK ranged between 3.2 and 5.1. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 12 for H1, n = 28 for H9, n = 27 for WLS-1C, n = 12 for STiPS-R038).

Figure 6. STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Produces More Megakaryocytes and Platelet-Like Particles than Other Published Protocols
hES and hiPS cells were differentiated into MKs using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit and using four different published protocols from the literature with modifications. (A) Frequencies and numbers of CD41a+CD42b+ MKs per input cell for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038) were analyzed by flow cytometry as shown in Figure 2. (B) Numbers of PLPs generated per input cell were enumerated as described in Figure 5. Compared to the published protocols, STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit produced 10- to 40-fold more CD41a+CD42b+ MKs and 6- to 23-fold more PLPs per input cell. P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 - 8).
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| Formulation Category | Serum-Free |
|---|

含重组细胞因子的无血清甲基纤维素培养基,用于人胚胎干细胞和iPS细胞来源的细胞
用于将人ES细胞或iPS细胞分化为造血祖细胞
用于将人 ES 细胞或 iPS 细胞分化为红系祖细胞

cGMP标准、无饲养层的人胚胎干细胞(ES)和诱导多能干细胞(iPS)维持培养基
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。